Bonding rubber to steel is like creating a superpower couple in the world of materials. It’s a process that brings together two seemingly different entities to create something strong, flexible, and downright unyielding. From cars to factories, this technique finds its place in various industries. But let’s be real here: achieving a solid bond between rubber and steel requires some serious know-how and attention to detail. Lucky for you, this guide has got your back.
Picture this: four crucial steps standing between you and the perfect bond. We’re talking surface preparation, adhesive selection, application, and curing. Each step holds the key to unlocking a connection that can withstand whatever life throws at it. But hold on tight because we’ll also explore the challenges that come with it – temperature variations and material compatibility are just a couple of hurdles we’ll tackle head-on.
So buckle up and get ready for a wild ride through the nitty-gritty details of bonding rubber to steel. By the end of this guide, you’ll have all the tools you need to create an unbreakable union that will make even Batman jealous. Let’s dive in.
What is Rubber-to-Steel Bonding?
Contents
- 1 What is Rubber-to-Steel Bonding?
- 2 Types of Rubber-to-Steel Bonding
- 3 Adhesive Bonding Agents for Rubber-to-Steel Bonding
- 4 Preparing the Surfaces for Adhesive Bonding
- 5 Applying the Adhesive and Curing the Bond
- 6 Mechanical Fastening for Rubber-to-Steel Bonding
- 7 Vulcanization for Rubber-to-Steel Bonding
- 8 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Method of Rubber-to-Steel Bonding
- 9 Conclusion
In the world of material bonding, few combinations are as powerful and fascinating as rubber and steel. Rubber-to-steel bonding is a specialized technique that brings together the unique properties of these materials to create components that can withstand the harshest conditions and deliver exceptional performance.
The process of rubber-to-steel bonding starts with the selection of the right adhesive. Adhesives specifically designed for this purpose are used to create a strong and durable bond between the rubber and steel surfaces. These adhesives are formulated to withstand extreme temperatures, high pressures, and other environmental factors that the bonded materials may encounter.
Surface preparation is a crucial step in the rubber-to-steel bonding process. The rubber and steel surfaces must be meticulously cleaned, dried, and free from any contaminants that could interfere with the bonding process. This ensures that the adhesive can effectively adhere to both surfaces, creating a solid connection.
Once the surfaces are prepared, the adhesive is applied to either one or both of them. The specially formulated adhesive is spread evenly, ensuring full coverage on the contact areas. Then, the rubber and steel surfaces are pressed together firmly to establish good contact between them. This can be achieved using clamps or weights to apply even pressure across the bonded area. The adhesive requires sufficient time to cure, allowing it to dry and set according to the manufacturer’s recommended curing time.
The benefits of rubber-to-steel bonding extend across various industries. In the automotive sector, this technique plays a crucial role in manufacturing components such as engine mounts, suspension bushings, and seals. These components require a strong bond to withstand the constant vibrations and shocks experienced by vehicles, ensuring optimum performance and reliability.
One of the key advantages of rubber-to-steel bonding is its ability to provide effective seals or joints between different materials. The flexibility of rubber allows it to conform to irregular surfaces, while steel provides strength and stability. Together, they create a tight connection that prevents leaks, reduces noise transmission, and improves overall performance.
To achieve successful rubber-to-steel bonding, several factors must be carefully considered. Proper surface preparation is essential to ensure optimal adhesion between the rubber and steel surfaces. The selection of the right adhesive is critical in determining the strength and compatibility of the bond. Post-bonding processes, such as trimming excess rubber and conducting quality control tests, guarantee that the bond meets the required standards.
Types of Rubber-to-Steel Bonding
When it comes to bonding rubber to steel, there are various methods to choose from. Each method has its own benefits and drawbacks, depending on the specific application and desired bond strength. In this article, we will take a closer look at some of the most common methods used in rubber-to-steel bonding. So grab your glue and let’s dive in.
Mechanical Bonding:
Let’s start with the basics – mechanical bonding. This method involves creating a physical interlock between the rubber and steel surfaces. It’s like giving them a big bear hug. By roughening the steel surface and applying adhesive, the rubber gets cozy with the adhesive-coated surface. The result? A strong bond that can withstand some serious pulling and tugging. However, keep in mind that flexibility might not be its strong suit.
Chemical Bonding:
Chemical bonding is all about using special adhesives or bonding agents to create a strong connection between rubber and steel. Think of it as a magical potion that brings them together. By applying the adhesive to both surfaces and allowing it to cure or dry, you get a bond that can stand the test of time. But remember, this method requires careful surface preparation and patience during curing time.
Vulcanization:
If you’re looking for a bond that can handle heat, chemicals, and tough conditions, vulcanization is your go-to method. This process involves heating the rubber and steel together under pressure, creating a chemical reaction that forms an unbreakable bond. It’s like forging a lifelong partnership between rubber and steel. However, keep in mind that vulcanization requires specialized equipment and expertise.
Adhesive Bonding:

Adhesive bonding is like playing matchmaker between rubber and steel. By choosing the right adhesive for their unique qualities, you can create a bond that checks all the boxes. This method offers flexibility in terms of bond strength, curing time, and application method. Just make sure to prep the surfaces properly and select the right adhesive for the job.
Overmolding:
Imagine molding rubber directly onto a steel substrate. That’s overmolding. It’s like creating a rubber armor for steel. By injecting molten rubber into a mold containing the steel, you get a bond that’s as strong as Spider-Man’s web. The rubber and steel become one during the molding process, creating an unbreakable connection.
Adhesive Bonding Agents for Rubber-to-Steel Bonding
In the world of rubber-to-steel bonding, finding the perfect adhesive bonding agent is like being a matchmaker. It requires careful consideration to create a strong and lasting connection between these two materials. Let’s dive into the secrets of adhesive bonding agents and discover the ideal match for rubber and steel.
Neoprene-based Contact Cement:
Neoprene-based contact cement is like a love potion for rubber-to-steel bonding. This adhesive acts as the ultimate matchmaker, creating a bond that is resistant to heat, oil, and chemicals. Whether you’re working with large surface areas or need flexibility in your bond, neoprene-based contact cement is the way to go. Simply apply it to both the rubber and steel surfaces, let it dry, and then press them together. Voila. A strong bond is formed.
Epoxy:
Epoxy adhesives are the superheroes of bonding agents. They possess exceptional strength and versatility, making them suitable for various applications. When it comes to rubber-to-steel bonding, choose an epoxy adhesive specifically formulated for this purpose. These adhesives offer excellent flexibility and bond strength, ensuring a joint that can withstand mechanical stress and environmental factors.
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives (Super Glues):

When time is of the essence, cyanoacrylate adhesives come to the rescue. These adhesives cure rapidly and create strong bonds on a wide range of materials. However, not all super glues are suitable for rubber-to-steel bonding. Look for specialized cyanoacrylate formulations designed specifically for this purpose. They offer enhanced bond strength and flexibility, ensuring optimal performance.
Specialized Rubber-Specific Adhesives:
Rubber comes in various forms, such as EPDM or natural rubber. To create a reliable bond with steel substrates, specialized adhesive bonding agents for these specific rubber types are available. These adhesives are formulated to provide excellent adhesion to their respective rubber compounds, ensuring a strong and lasting bond.
Preparing the Surfaces for Adhesive Bonding
In the realm of rubber-to-steel bonding, finding the perfect adhesive bonding agent is like playing cupid, carefully pairing these materials to create a strong and enduring connection. However, creating that bond requires proper preparation of the surfaces involved. Let’s uncover the secrets of preparing the surfaces for adhesive bonding between rubber and steel and discover how glue can be used to bond these two materials together.
- Thorough Cleaning: The first step in preparing the surfaces is to clean them thoroughly. Any dirt, grease, or contaminants on the surfaces can hinder the adhesion process. Grab a mild detergent or solvent and give those surfaces a good scrub. Make sure you’re using a cleaning agent that won’t leave any residue behind.
- Roughening Up: After cleaning, it’s time to roughen up the surfaces. This step increases their surface area and provides more bonding points for the adhesive. You can use sandpaper, a wire brush, or even abrasive blasting to achieve this roughened effect. Just be careful not to damage the materials in the process.
- Cleaning Again: Once you’ve roughened up the surfaces, it’s important to clean them again to remove any loose particles or debris. You don’t want any pesky particles interfering with your bond. Grab some compressed air and blow away any remaining particles.
- Primers: In some cases, applying a primer can improve adhesion. Primers help promote chemical bonding between the adhesive and the surfaces, especially when dealing with difficult-to-bond materials like rubber and steel. Just make sure you’re using a primer that’s compatible with both the adhesive and the materials you’re working with.
- Drying Time: After applying the primer, give it some time to dry before moving on to the next step. The drying time will depend on the type of primer you’re using, so be sure to check the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Ensuring Dry Surfaces: Finally, before applying the adhesive, ensure that both surfaces are completely dry. Moisture can interfere with the bonding process and weaken your bond. Grab a clean cloth or use compressed air to ensure that the surfaces are nice and dry.
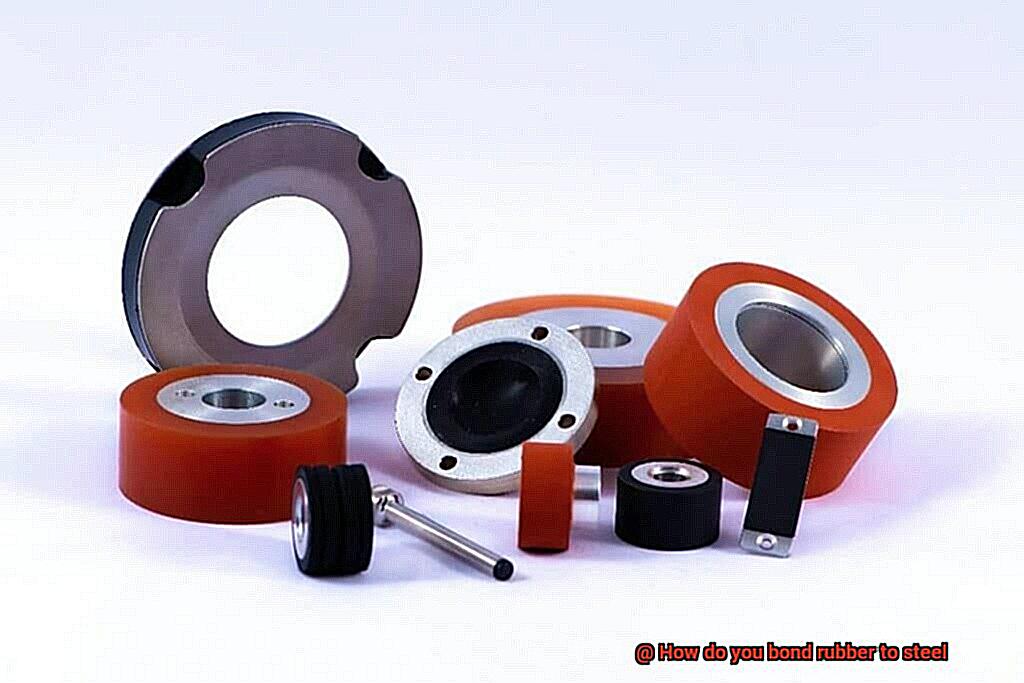

Applying the Adhesive and Curing the Bond
Applying the Adhesive and Curing the Bond: The Perfect Match for Rubber and Steel
You’re ready to create a rock-solid connection between rubber and steel? Get ready to become a glue guru as we dive into the thrilling world of adhesive application and bond curing.

First things first, you need to select the perfect adhesive for the job. Epoxy, cyanoacrylate, and rubber-based adhesives are popular choices, but consider factors like the type of rubber and steel, application requirements, and desired bond strength.
Once you have your adhesive, it’s time to prep those surfaces. Think of it like a first date – clean and free from any contaminants that could ruin the connection. Use degreaser or solvent for a thorough cleaning. And don’t forget to roughen them up. Sandpaper or wire brush will create a surface ready to bond.
Now comes the exciting part – applying the adhesive. Grab your brush or applicator and spread that adhesive evenly on both surfaces. Use enough for complete coverage, but avoid drips or oozing. No messy situations here.
Now bring those surfaces together. Picture a passionate embrace – you want a strong connection. Clamp or use weights to hold them in place. Apply enough pressure for good contact between adhesive and surfaces. This is where the magic happens.
Now be patient. The bond needs time to cure or set. Check instructions for curing times since it varies depending on adhesive type. Avoid disturbing or moving the bond during this time – no relationship drama here. Let that bond form undisturbed.
Once fully cured, test the strength of your bond. Apply force or stress to see if it holds up. If it does, congratulations – you’ve achieved a strong connection between rubber and steel.
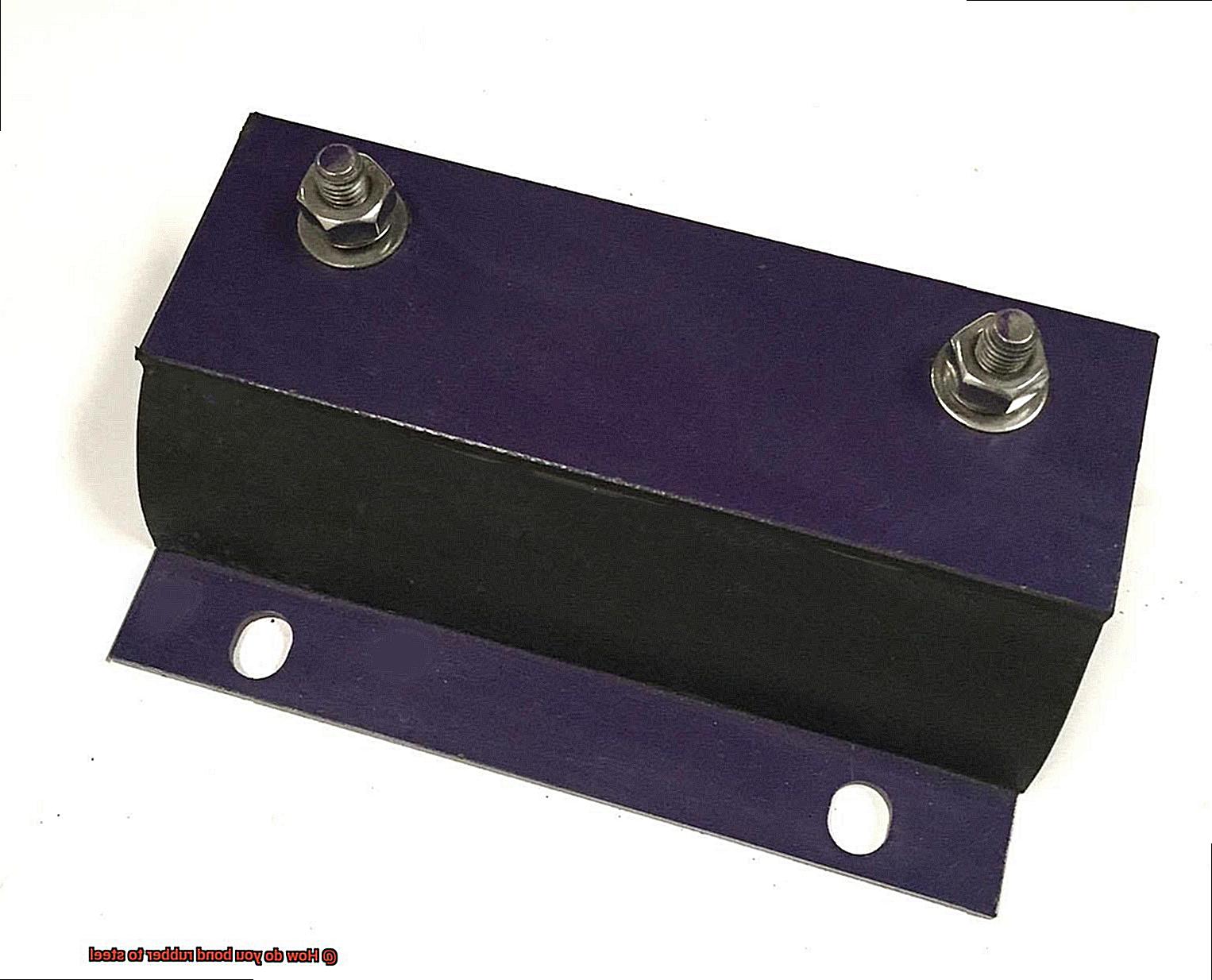
Mechanical Fastening for Rubber-to-Steel Bonding
Rubber and steel may seem like an odd couple, but when it comes to bonding them together, it’s all about finding the perfect match. While glue or adhesive is often the go-to choice, there’s another method that offers a different set of advantages – mechanical fastening.
Mechanical fastening involves using physical connectors like screws, bolts, rivets, or clips to hold the rubber and steel together. It’s like giving your bond a little extra support – think of it as a relationship where you’re not just relying on love, but also practicality and strength.
One advantage of mechanical fastening is its simplicity and ease of application. Unlike glue, which requires precise surface preparation and curing time, mechanical fasteners can be installed quickly and easily. It’s like finding that perfect partner who just fits effortlessly into your life.
There are different types of mechanical fasteners you can use for rubber-to-steel bonding, each with its own unique advantages:
- Screws or bolts: These threaded connectors can be tightened to securely hold the rubber and steel components together. They offer a rigid connection and are great for applications that require high strength and load-bearing capabilities.
- Rivets: These permanent fasteners provide a secure and tamper-resistant bond. With their cylindrical shaft and head design, they are commonly used in applications where a watertight seal is required – sealing the deal on a long-term commitment.
- Clips or clamps: These connectors apply pressure to hold the rubber in place against the steel surface. They allow for easy removal and replacement of the rubber component, adapting to changing circumstances – always there when you need them.

When using mechanical fastening for rubber-to-steel bonding, it’s important to consider factors like design and material compatibility. The size, type, and number of fasteners should be determined based on the load requirements and intended application of the bonded assembly. And just like in any relationship, it’s vital to choose the right material for the fasteners to ensure compatibility with both the rubber and steel surfaces.
Vulcanization for Rubber-to-Steel Bonding
Rubber and steel, two seemingly disparate materials, can be seamlessly bonded through the remarkable process of vulcanization. Utilizing a combination of heat, pressure, and a specialized adhesive, vulcanization creates a bond that is not only strong and durable but also resistant to the harshest environmental conditions. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of vulcanization for rubber-to-steel bonding, uncovering its unique elements that produce an unbreakable union.
Preparation:
Before the magic of vulcanization can occur, meticulous preparation of both rubber and steel surfaces is essential. Through thorough cleaning, all contaminants and oils are eradicated, ensuring an immaculate canvas for the bonding process. This clean slate sets the stage for a successful and unyielding connection.
Adhesive Application:
Once the surfaces are pristine, a layer of vulcanizing agent or adhesive is meticulously applied to both rubber and steel. This special agent acts as a cupid, bringing these materials closer together by promoting adhesion. Like an invisible force drawing them in, it paves the way for their ultimate fusion.
Pressing Matters:
With the adhesive skillfully applied, it is time for the grand meeting of rubber and steel. They are pressed together with precision using specialized equipment like a hydraulic press. This ensures seamless contact between the surfaces, laying the foundation for a bond of unparalleled strength.
Heat it Up:
Now comes the moment of transformation – heat. The bonded assembly is subjected to carefully controlled temperatures and durations. This initiates a chemical reaction within the vulcanizing agent or adhesive, creating cross-links between the rubber molecules. These cross-links bestow upon the bond remarkable strength and resilience, enabling it to withstand even the most rigorous challenges.
Cooling Down:
After being subjected to intense heat, it is crucial to let things cool down. This allows the vulcanizing agent or adhesive to fully cure and solidify the bond. Like a relationship that needs time to settle, cooling down ensures that the connection becomes truly inseparable.
The Result:
The result of vulcanization is a bond that is not only strong and durable but also impervious to temperature changes, moisture, and chemicals. It is a match made in heaven, a partnership that can withstand the test of time and adversity.
Applications:
Vulcanization for rubber-to-steel bonding finds wide application in industries such as automotive, construction, and manufacturing. From sealing gaskets in engines to bonding conveyor belts in industrial settings, this process provides a reliable solution for diverse applications.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Method of Rubber-to-Steel Bonding
Rubber-to-steel bonding is a crucial process in various industries, ensuring the durability and performance of products in demanding applications. Choosing the right bonding method is essential to achieve a strong and long-lasting bond between rubber and steel surfaces. When making this decision, several factors need to be considered to ensure a successful bond.
Firstly, the compatibility of materials is vital. Rubber and steel have different properties, so it is important to select a bonding method that is compatible with both materials. Factors such as the type of rubber and steel being bonded, their surface characteristics, and their chemical composition should be considered to ensure a successful bond.
Secondly, the environmental conditions that the bonded product will be exposed to must be taken into account. This includes temperature extremes, humidity, or exposure to chemicals. Choosing a bonding method that can withstand these conditions without compromising the integrity of the bond is crucial. Factors such as heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and weathering capabilities should be evaluated.
Thirdly, understanding the specific requirements of the application is vital in selecting the appropriate bonding method. Factors such as load-bearing capacity, flexibility, vibration resistance, electrical conductivity, or thermal insulation should be considered. These requirements will help determine which bonding method will best meet the needs of the application.
Additionally, production efficiency and cost considerations play a significant role in choosing a bonding method. The production process should be efficient and cost-effective. Factors such as curing time, equipment requirements, and compatibility with existing production processes should be evaluated. Choosing a bonding method that aligns with these factors can streamline manufacturing operations and reduce costs.
Ultimately, cost is an important consideration in any manufacturing decision. Comparing the costs associated with different bonding methods, including materials, equipment, and labor is essential. It is important to balance cost savings with the desired bond strength and durability.
jq8L9nP718g” >
Conclusion
In conclusion, bonding rubber to steel is a complex process that requires careful consideration and the use of specialized techniques and materials. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can achieve a strong and durable bond between these two materials.
To begin with, it is crucial to properly prepare the surfaces that will be bonded. This involves cleaning both the rubber and steel surfaces thoroughly to remove any dirt, grease, or contaminants that could interfere with the bonding process. Additionally, roughening the surface of the steel using sandpaper or a wire brush can improve adhesion by creating more surface area for the adhesive to grip onto.
Next, selecting the right adhesive is essential for a successful bond. There are various types of adhesives available for bonding rubber to steel, such as epoxy-based adhesives or rubber-based adhesives. It is important to choose an adhesive that is specifically designed for bonding these two materials together and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application.
Applying the adhesive evenly and in the correct amount is crucial for achieving a strong bond. Using too little adhesive may result in weak adhesion, while using too much can lead to excessive squeezing out of the adhesive during curing. It is recommended to apply a thin layer of adhesive onto both surfaces and then press them firmly together.
Once the rubber and steel are bonded together, it is important to allow sufficient time for curing. This typically involves keeping pressure on the bond and allowing it to cure at room temperature for a specific period of time as recommended by the adhesive manufacturer. During this curing process, it is essential to avoid any movement or stress on the bond that could compromise its strength.
In summary, bonding rubber to steel requires careful surface preparation, selection of appropriate adhesive, proper application techniques, and adequate curing time. By following these guidelines, you can create a reliable bond between rubber and steel that will withstand various environmental conditions and mechanical stresses.






