Are you tired of your aluminum and brass materials corroding rapidly when they come in contact with each other? Galvanic corrosion is a common problem that can cause significant damage to metals. This electrochemical reaction occurs when two dissimilar metals, such as aluminum and brass, are in contact with each other.
Luckily, there are effective prevention methods to stop galvanic corrosion from happening. In this post, we’ll explore the reasons why aluminum and brass tend to corrode when they interact. We’ll also dive into various techniques that can be implemented to prevent corrosion, including protective coatings, isolation, and cathodic protection systems.
Whether you’re an industry professional or just someone who wants to protect their metal materials from damage, this post has got you covered. Keep reading to discover the best ways to prevent galvanic corrosion between aluminum and brass.
What is Galvanic Corrosion?
Contents
Galvanic corrosion is a sneaky culprit that can wreak havoc on metal structures and equipment. It occurs when two dissimilar metals come into contact with each other in the presence of an electrolyte, such as saltwater or acidic solutions. In this process, one metal becomes the anode and the other becomes the cathode, leading to an electron flow from the anode to the cathode. The result? The anode corrodes at a faster rate than the cathode.
Take aluminum and brass, for instance. When they come into contact with each other, galvanic corrosion can occur because of their different electrochemical potentials. Aluminum has a more negative potential than brass, meaning that it corrodes faster than brass in this scenario. If left unaddressed, galvanic corrosion can lead to leaks, cracks, and even structural failure.

Thankfully, there are several ways to prevent galvanic corrosion between aluminum and brass. One approach is to use a barrier between the two metals, such as a non-conductive material like rubber or plastic to keep them separated. Another option is to use a coating on one or both of the metals to prevent direct contact. Paint or anodizing are useful coatings for this purpose.
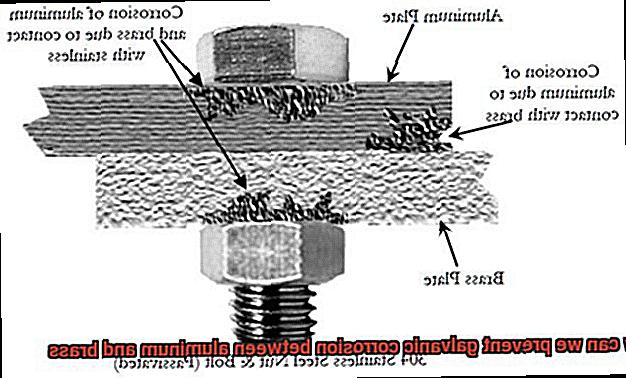
Another method for preventing galvanic corrosion is to introduce a sacrificial anode – a more reactive metal that is connected to the aluminum and brass. This metal will corrode instead of the aluminum and brass, protecting them from galvanic corrosion. Zinc is commonly used as a sacrificial anode in marine applications.
It’s also important to monitor and maintain the electrolyte environment around aluminum and brass. This involves controlling humidity levels, monitoring pH levels, and avoiding exposure to saltwater or other corrosive environments.
Differences in Electrode Potential between Aluminum and Brass
Well, it all comes down to galvanic corrosion. This destructive force occurs when two dissimilar metals come into contact in the presence of an electrolyte. Today, we’ll be exploring the differences in electrode potential between aluminum and brass, and how it contributes to this phenomenon.
Let’s start by understanding electrode potential. This refers to a metal’s tendency to lose or gain electrons. In the case of aluminum and brass, there is a significant difference in their electrode potentials. Aluminum has a more negative electrode potential, while brass has a more positive electrode potential. When these two metals come into contact, the flow of electrons is driven from aluminum to brass, causing galvanic corrosion.
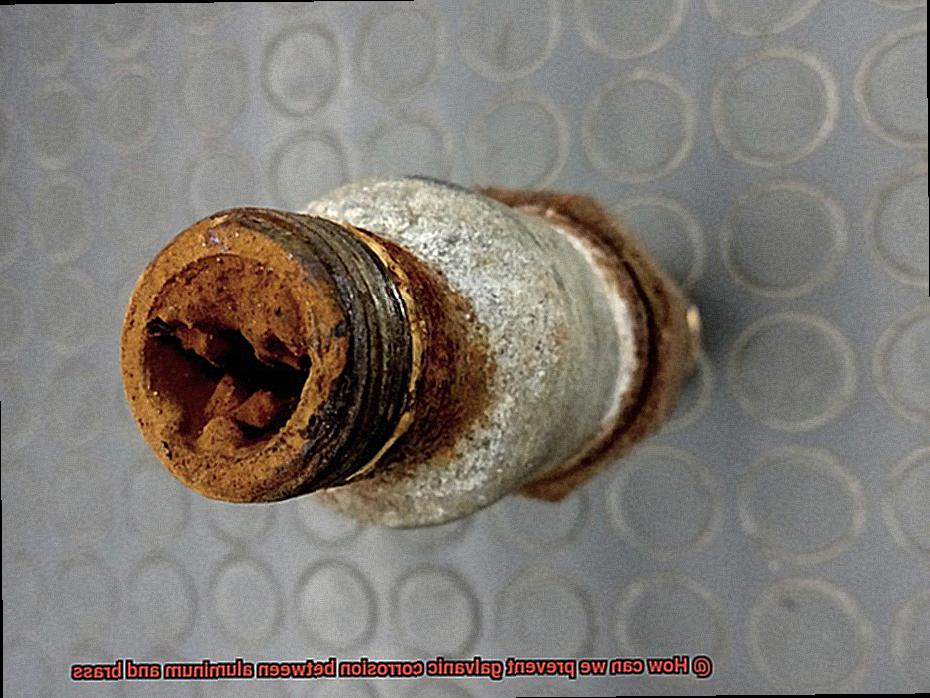

So why does this happen? The electrolyte provides a medium for the transfer of electrons between the metals, completing the circuit. As a result, the more negative metal (aluminum) starts to corrode, while the more positive metal (brass) remains intact.
To prevent galvanic corrosion between aluminum and brass, it is essential to minimize or eliminate their contact with each other. This can be achieved by using insulating materials or coatings that act as a barrier between the two metals. Additionally, avoiding exposure to electrolytes such as moisture or saltwater is crucial.
Another effective way to prevent galvanic corrosion is by using sacrificial anodes. These small pieces of metal have a more negative electrode potential than aluminum and brass. When connected to the metals through an electrical circuit, they corrode instead of aluminum or brass.
Using a Barrier to Prevent Galvanic Corrosion
Look no further, because using a barrier is the solution you need. As an expert in this field, I have gathered some research notes to explain how using a barrier can be the savior of your metal parts.
Firstly, creating a barrier is as simple as using a non-conductive material between the two metals. This material can range from a plastic gasket to a layer of paint or varnish. The sole purpose of the barrier is to prevent the two metals from coming into contact with each other, which halts the flow of electrons that cause galvanic corrosion.
One efficient method of creating a barrier is by using an insulating coating like an epoxy or polyurethane coating. These coatings are applied to the surface of the metal and act as a barrier between the aluminum and brass. The coating is thick enough to stop any electrical current from flowing between the two metals but thin enough to maintain good adhesion to the metal surfaces.
Another way to create a barrier is by using gaskets made of non-conductive materials such as rubber, plastic, or cork. Gaskets are placed between the two metals and prevent them from coming into direct contact with each other. Gaskets are commonly used in applications where there is frequent assembly and disassembly of parts, such as in automotive engines.
It’s crucial to note that the effectiveness of using a barrier to prevent galvanic corrosion depends on the thickness and quality of the barrier material used. It’s also vital that any gaps or cracks in the barrier are sealed, as these can provide a pathway for electrical current to flow.
Applying Coatings to Prevent Galvanic Corrosion
Coatings provide a barrier between dissimilar metals, preventing them from coming into direct contact and reducing the likelihood of galvanic corrosion. Let’s explore some popular coating materials and their benefits.
Epoxy coatings are a common choice for many industries. They can be applied to both aluminum and brass surfaces, effectively separating the two metals and reducing the risk of corrosion. Epoxy coatings are also resistant to chemicals, abrasion, and impact, making them ideal for industrial applications.
Polyurethane coatings are another effective option. They provide excellent protection against moisture, UV radiation, and corrosion. These coatings are highly durable and resistant to wear and tear, making them suitable for use in harsh environments.
Ceramic coatings offer exceptional resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and high temperatures. They can be applied to both aluminum and brass surfaces and provide excellent insulation against electrical conductivity.
Specialized coatings containing zinc or other sacrificial metals are also available. These coatings react with the corrosive environment and protect the underlying metal surfaces.
It is essential to consider factors such as durability, chemical resistance, and electrical conductivity when choosing a coating material. By selecting the right type of coating material, you can ensure that your metal parts remain corrosion-free and strong for longer.

Utilizing a Sacrificial Anode

Look no further than the sacrificial anode—the superhero of the metal world. By connecting a more active metal, such as zinc or magnesium, to your aluminum component, the anode corrodes instead of the aluminum, protecting it from galvanic corrosion.
But, not all sacrificial anodes are created equal. Choosing the right type for your unique application is crucial for maximum effectiveness. Factors like the environment and conditions of use can affect their performance, so do your research before selecting one.
Installation is also paramount. The sacrificial anode should be directly in contact with the aluminum component and electrically connected to it. Placing it in a location where it can easily corrode and be replaced when necessary is also essential.
Don’t forget about regular inspection and replacement. As the anode corrodes, its ability to protect the aluminum wanes. Replacing it when it has corroded at least 50% of its original size will keep your components safe from corrosion damage.
Monitoring and Maintaining the Electrolyte Environment
We have the perfect solution – monitoring and maintaining the electrolyte environment.
To prevent galvanic corrosion from occurring, it is crucial to maintain a stable and neutral environment. Here are some essential factors to keep in mind:
Firstly, regularly testing pH levels and adjusting them as necessary can help maintain a stable environment. Additionally, preventing contaminants such as salt or other metals from entering the solution can also help prevent galvanic corrosion.
Temperature control is another crucial factor to consider. High temperatures can speed up the corrosion process, so it’s important to keep the solution at a stable temperature and avoid exposing it to extreme heat.
Lastly, regular inspection and maintenance of equipment or structures made from aluminum and brass can help detect any signs of corrosion, which should be addressed immediately through cleaning, polishing, or applying protective coatings.
6sB906LrrCA” >
Conclusion
In conclusion, the destructive impact of galvanic corrosion between aluminum and brass cannot be overstated. This electrochemical reaction is triggered when two dissimilar metals come into contact with each other in the presence of an electrolyte. However, there are several effective prevention methods you can apply to stop this corrosive process from happening.
One approach that works well is to use a barrier between these two metals. For instance, a non-conductive material like rubber or plastic can keep them separated and prevent direct contact. Another option is to use coatings on one or both of the metals to keep them from coming into contact with each other. Paint or anodizing are useful coatings for this purpose.
Another method for preventing galvanic corrosion is to introduce a sacrificial anode – a more reactive metal that connects to the aluminum and brass. This metal will corrode instead of the aluminum and brass, protecting them from galvanic corrosion.
It’s equally important to monitor and maintain the electrolyte environment around aluminum and brass parts. This involves controlling humidity levels, monitoring pH levels, and avoiding exposure to saltwater or other corrosive environments.
By implementing these techniques, you can ensure that your metal parts remain corrosion-free and strong for longer periods.






