Picture this: you’re at a hospital, nursing a fresh wound, and wondering how on earth they’re going to close it up. Well, fear not, because hospitals have a secret weapon in their arsenal – medical adhesives. These little wonders have taken the medical world by storm, revolutionizing the way wounds are sealed and helping us heal faster than ever before.
Unlike those old-fashioned stitches or staples, medical adhesives offer a whole new level of wound closure wizardry. They work like super glue for your skin, bonding quickly and securely to keep those pesky wound edges closed and protected. No more painful punctures or unsightly scars – just fast healing and smoother recoveries.
But what exactly can these magical adhesives do? Well, pretty much anything you can throw at them. From surgical incisions to lacerations and even certain types of burns, medical adhesives are versatile enough to handle wounds big and small. They’ve become an essential tool in every hospital’s toolkit.
In this blog post, we’re going to dive headfirst into the captivating world of medical adhesives. We’ll explore the different types available, uncover their secrets on how they work their magic, and discover the unique benefits they bring to the wound healing process. So grab your lab coat (or just a cup of coffee), because we’re about to unravel the mysteries behind these incredible glues that have become an indispensable part of modern medicine.
Let’s get stuck into it.
Types of Adhesives Used in Hospitals
Contents
These remarkable substances play a vital role in wound closure and patient care. In this article, we will explore five different types of adhesives used in hospitals and the factors that influence their suitability for specific wounds. From super glue to gentle closures, these adhesives are instrumental in promoting healing and preventing infections.
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives: Super Glue for Super Healing
Imagine a tiny cut on your finger. That’s where cyanoacrylate glue, also known as medical super glue, comes to the rescue. This adhesive acts like a superhero with its quick-drying powers and strong bonding abilities. It works wonders for closing small cuts and superficial wounds, allowing the skin to heal naturally underneath. Cyanoacrylate adhesives are available in different formulations, such as octyl cyanoacrylate and butyl cyanoacrylate, each with specific properties suited for different types of wounds. They provide a protective barrier against bacteria and other contaminants, reducing the risk of infection.
Fibrin Sealants: Nature’s Healing Power
For more complex wounds or surgical incisions, hospitals turn to fibrin sealants. These sealants are derived from human or animal blood plasma and contain fibrinogen and thrombin, which work together to form a fibrin clot at the wound site, promoting hemostasis. Fibrin sealants are particularly useful in surgeries where traditional sutures may be challenging to apply or may cause additional trauma. They are often used in cardiovascular, liver, and spleen surgeries.
Medical-grade Adhesive Tapes: Tapes that Stick Around
Nurses use adhesive tapes in hospitals to secure wound dressings. These tapes are like trusty sidekicks, providing support and holding everything together. They come in different materials like paper, cloth, or plastic, offering flexibility and breathability based on the specific needs of the wound. Medical-grade adhesive tapes adhere securely to the skin without causing irritation or damage when removed. They are versatile and can be easily cut into desired shapes, making them suitable for various wound sizes and locations.
Hydrocolloid Dressings: The Healing Hug
Hydrocolloid dressings are adhesive dressings that create a moist environment around the wound, promoting faster healing and preventing tissue dehydration. These dressings consist of gel-forming agents, such as pectin and gelatin, embedded within a flexible, waterproof backing. Hydrocolloid dressings are particularly effective for shallow wounds, pressure ulcers, and minor burns. They provide a protective barrier against bacteria and contaminants while allowing for gas exchange to facilitate healing.
Cyanoacrylate Glue
In the world of wound closure, there exists a superhero adhesive known as cyanoacrylate glue. With its rapid action and strong, flexible seal, this glue has become a favorite among healthcare professionals. However, like any superhero, it has its pros and cons. Let’s explore the powers of cyanoacrylate glue that make it a go-to choice for wound closure.
Pros:
- Lightning-fast closure: Cyanoacrylate glue is the Flash of the wound closure world. It swiftly seals small cuts and incisions, making it a perfect choice when traditional sutures or staples are unnecessary or impractical.
- Master of challenging areas: This adhesive excels in tricky spaces. It’s like Spider-Man, effortlessly web-slinging to close wounds in joints or areas with excessive movement. No matter how complicated the location, cyanoacrylate glue ensures a secure closure.
- Shield against infection and healing accelerator: When applied to a wound, cyanoacrylate glue forms an impenetrable barrier that acts as a warrior against bacteria and other microorganisms. It also serves as a healer’s sidekick, aligning wound edges and promoting faster healing.
- Aesthetic genius: Like an artist with a paintbrush, cyanoacrylate glue leaves no visible marks or blemishes. Its clear-drying property makes it ideal for wounds on the face or other visible areas. Say goodbye to unsightly sutures or staples.
- Waterproof defender: With the power to create a waterproof seal, cyanoacrylate glue allows patients to conquer water-related challenges without worrying about compromising the wound closure. It’s like Aquaman keeping wounds safe from water’s harmful effects.
Cons:
- Limited powers: Unfortunately, not all wounds can be conquered by cyanoacrylate glue. Deep wounds or those with significant tissue loss may require the assistance of traditional sutures or more advanced closure techniques. It’s important to assess the wound’s nature before deciding on the superhero adhesive.
- Individual vulnerabilities: Just like every superhero has their Kryptonite, cyanoacrylate glue is not suitable for every patient. Some individuals may have allergies or sensitivities that make it unsafe to use. It’s crucial to consider individual patient factors to ensure the safest and most effective wound closure.
Fibrin Glue
Imagine you’re a doctor in a bustling hospital, tasked with closing a wound. Suddenly, a superhero adhesive swoops in to save the day – fibrin glue. This remarkable substance mimics the body’s natural clotting process, sealing wounds with lightning-fast speed and promoting faster healing. Join me as we delve into the captivating world of fibrin glue and discover its superpowers in wound closure.
The Making of Fibrin Glue:
Fibrin glue is no ordinary adhesive – it’s a powerful duo composed of two key components: fibrinogen and thrombin. Fibrinogen, a protein found in blood plasma, plays a vital role in forming blood clots. Thrombin, an enzyme, converts fibrinogen into fibrin, creating a mesh-like structure that stabilizes the clot. When combined, these components create the ultimate adhesive mixture.
The Application Process:
Picture yourself in the operating theater, ready to utilize fibrin glue to close a wound. First, you meticulously clean and prepare the wound site to ensure its pristine condition. Then, with the precision of a superhero, you skillfully mix the two components of fibrin glue and apply it directly to the wound using a syringe or applicator. Within moments, the glue adheres to the tissue, creating a shield-like barrier that seals the wound.
Superpowers at Work:
One of fibrin glue’s greatest advantages is its ability to create an immediate bond between tissues. Say farewell to traditional sutures or staples – this superhero adhesive can eliminate their need in certain cases. With expedited healing times and minimized scarring, fibrin glue truly saves the day for patients and doctors alike. Additionally, it provides a watertight seal, preventing any fluid leakage from the wound site.
Beyond Wound Closure:
But wait, there’s more. Fibrin glue isn’t limited to closing wounds; it possesses a myriad of other medical applications. Surgeons employ it in various procedures to promote tissue adhesion, particularly in delicate areas like the eyes or internal organs. Reconstructive surgeries also benefit from fibrin glue, as it securely holds grafts or flaps in place. Truly, fibrin glue is a versatile superhero adhesive.

Limitations and Vulnerabilities:
Like any superhero, fibrin glue has its limitations and vulnerabilities. It may not be suitable for all types of wounds. It works best for small to medium-sized wounds with clean, well-approximated edges. Deep or heavily contaminated wounds may necessitate additional closure methods. Always consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate wound closure method.
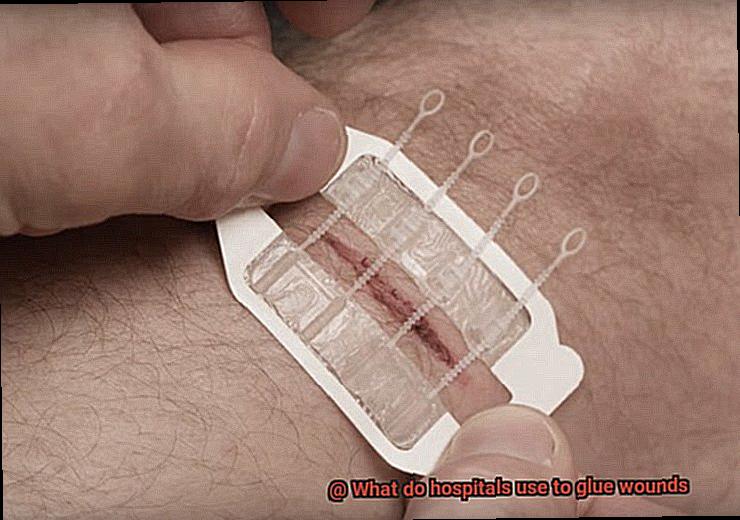
Adhesive Strips and Tapes
Adhesive strips and tapes are versatile tools used in hospitals for wound closure. These sticky wonders, such as butterfly closures or steri-strips, offer numerous advantages for healthcare professionals and patients alike. Let’s explore the world of adhesive strips and tapes and discover why they are the go-to choice in the medical field.
Let’s start with adhesive strips, also known as butterfly closures or steri-strips. Made of non-woven fabric or paper tape with a hypoallergenic adhesive, these strips are gentle on the skin and can be applied without causing discomfort. They come in various sizes, ensuring compatibility with different wounds – talk about versatility.
Next up is surgical tape, a heavyweight in the adhesive game. Made of a strong and durable material, this tape provides excellent adhesion that can withstand movement and moisture. It’s perfect for securing dressings or medical devices during the healing process.
Here’s a list of advantages when using adhesive strips and tapes:
- Non-invasive: Say goodbye to stitches or sutures. Adhesive strips and tapes offer a less invasive alternative, resulting in reduced pain and discomfort for patients.
- Faster healing: By securely holding the wound edges together, these products promote faster healing times. Additionally, they create a barrier against bacteria and other microorganisms, reducing the risk of infections.
- Easy application: Healthcare professionals follow standardized procedures to ensure proper wound closure and minimize complications. This means you can trust that these strips and tapes will be applied correctly every time.
However, it’s important to note that not all wounds are suitable for adhesive strips and tapes. Large or deep wounds may require more extensive closure methods like sutures or staples. Always consult a healthcare professional for the best course of action.
Bioadhesives
In this article, we will explore the wonders of these adhesive marvels and how they bring comfort, speed, and efficiency to the healing process, bidding farewell to traditional stitches and staples.
Types of Bioadhesives:

Cyanoacrylate-based Adhesives:
Imagine medical-grade superglue that acts swiftly, forming a strong bond upon contact with moisture. Cyanoacrylate-based adhesives work by creating long chains of molecules when exposed to water or tissue fluids. Ideal for smaller cuts and lacerations that don’t require deep sutures, these adhesives provide a painless alternative to traditional stitches. Additionally, they reduce the need for anesthesia and expedite wound closure.
Fibrin Glue:
Derived from fibrinogen and thrombin, this adhesive imitates the body’s natural blood clotting process. When combined, they produce a clot-like substance that adheres to the wound site, facilitating the formation of a stable fibrin matrix. Fibrin glue is particularly effective for delicate tissues that require enhanced support during healing or situations that necessitate a stronger bond. Surgeons commonly utilize it in procedures where traditional sutures may not be suitable.
Biodegradable Bioadhesives:
These remarkable adhesives gradually break down over time and are absorbed by the body. They are particularly useful for superficial wounds or skin grafts where prolonged support is unnecessary. As they biodegrade, these adhesives provide temporary adhesion while simultaneously promoting wound healing.
The Benefits:
Ease of Use:
Bioadhesives simplify wound closure procedures by offering easy application, reducing procedure time, and streamlining the process for healthcare providers seeking efficiency.
Reduced Scarring:
Unlike traditional stitches, bioadhesives minimize scarring and result in more aesthetically pleasing outcomes. By sealing the wound edges together, they promote better cosmetic results.
Improved Patient Comfort:
Bioadhesives provide a gentle touch to the skin, causing minimal discomfort. Unlike stitches or staples, they eliminate the need for suture removal, reducing patient anxiety and post-procedure discomfort.
When to Use Adhesive Closure
When it comes to closing wounds, adhesive closure, also known as surgical glue or tissue adhesive, is gaining popularity as an alternative to traditional methods like sutures or staples. But when should you use adhesive closure? Let’s delve into the factors that determine its ideal application.
- Cosmetically appealing outcomes: Adhesive closure is perfect for wounds on visible areas of the body, such as the face or hands. Unlike sutures or staples, surgical glue creates a thin, flexible barrier that seamlessly blends in with the surrounding skin. This results in a less noticeable scar once the wound has healed.
- Quicker and less invasive: Adhesive closure eliminates the need for needles and thread, reducing the risk of needlestick injuries for healthcare professionals. The application process is relatively simple and can be done by trained medical staff, saving valuable time in the operating room or emergency department.
- Suitable for superficial wounds: Adhesive closure is recommended for superficial wounds with clean edges that are not under tension. If the wound is too large or deep, there may be a higher risk of reopening (dehiscence) or infection, making traditional sutures or staples a better choice.
- Proper wound cleaning and preparation: Adhesive closure is not a substitute for thorough wound cleaning and preparation. Healthcare professionals must ensure the wound is clean and disinfected before applying the adhesive. Trimming excessive tissue and removing debris may also be necessary for optimal adhesion.
Who Performs Adhesive Closure?
Adhesive closure is a technique used to seal wounds without the need for traditional sutures or staples. So, who are the professionals responsible for performing this fascinating procedure in hospitals? Let’s dive into the exciting world of glue and explore the glue gurus behind adhesive closure.
First on the list are physician assistants (PAs). These medical superheroes work under the supervision of licensed physicians and possess incredible skills in wound management. PAs can effectively apply adhesive closure, sealing those pesky wounds with precision and expertise.
Next up are nurse practitioners (NPs), advanced practice registered nurses who have gone the extra mile in their education and training. NPs are not your average nurses – they have the knowledge and skills to assess, diagnose, and treat patients. They also perform adhesive closure using surgical glue, ensuring wounds are securely sealed.
But let’s not forget about our trusty registered nurses (RNs) – these healthcare professionals have seen it all. With their training in wound care, RNs can clean and prepare the wound site, apply the magical glue, and ensure optimal healing. Their experience makes them experts in adhesive closure.
Of course, we can’t overlook the surgeons. These skilled individuals, both general surgeons and specialized surgeons, may also perform adhesive closure for more complex wounds that require their expertise. With their extensive training in wound management, surgeons determine when adhesive closure is appropriate based on various factors.
Whether it’s a PA, NP, RN, or surgeon, you can rest assured that you’re in good hands when it comes to adhesive closure. The choice of who performs the procedure may vary depending on factors such as the severity of the wound and the healthcare setting.
Protocols for Adhesive Closure
Adhesive closure, the use of medical adhesives or glues to close wounds, has revolutionized wound care in hospitals. With a variety of adhesive options available, hospitals can tailor their approach based on the type and location of the wound, as well as the patient’s specific needs.
One commonly used adhesive is cyanoacrylate glue, also known as medical-grade super glue. This fast-acting adhesive forms a strong bond upon contact with moisture like blood or bodily fluids. It is ideal for small, superficial wounds with clean edges that are not under tension. Emergency departments and urgent care settings often rely on cyanoacrylate glue for its quick and efficient wound closure abilities.
Another valuable option is fibrin glue, derived from proteins found in human blood. This adhesive mimics the natural clotting process and promotes healing by forming a stable fibrin clot at the wound site. It is particularly useful for delicate or complex wounds involving organs or blood vessels.
In some cases, hospitals may opt for adhesive strips or tapes to hold wound edges together. These strips are typically made of non-allergenic materials like nylon or polyester and offer easy application and removal.
Before applying any adhesive, hospitals adhere to strict protocols to ensure patient safety and optimal outcomes. These protocols include proper wound preparation, sterilization of instruments and materials, and a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s overall health status.
To ensure successful wound healing and minimize complications, healthcare professionals receive essential training and education on adhesive closure techniques.
Adhesive closure offers numerous benefits, including reduced scarring, faster healing times, and improved patient comfort. However, it is important to note that not all wounds are suitable for adhesive closure. Trust your healthcare provider to make the best decision for your individual case.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hospitals utilize a variety of adhesive options to glue wounds.
These options include medical-grade cyanoacrylate glues, such as Dermabond and SurgiSeal, which are specifically designed for wound closure. These glues are formulated to create a strong bond that holds the edges of the wound together, allowing for proper healing.
Regardless of the specific product used, these hospital-grade adhesives provide a reliable and efficient method for closing wounds without the need for traditional sutures or staples.