You know how important it is to have a rock-solid intake manifold gasket for your engine to perform at its best. This tiny but mighty component acts like a superhero, creating a tight seal between the engine block and the intake manifold. Its job? Ensuring smooth airflow and preventing any sneaky leaks that could rob you of power or damage your precious engine.
Lucky for us, sealing an intake manifold gasket offers plenty of options. In this blog post, we’ll dive into some of the most popular methods out there. We’ll spill the beans on their effectiveness, so you can choose wisely and find the perfect approach for your needs.
Get ready to explore the wonderful world of intake manifold gasket sealants, adhesives, and other sealing techniques. Whether you’re dealing with a pesky leak or just want to avoid future headaches, this guide has got your back. Let’s jump right in and learn how to seal the deal like a pro.
What is an Intake Manifold Gasket?
Contents
- 1 What is an Intake Manifold Gasket?
- 2 Types of Sealants for Intake Manifold Gaskets
- 3 RTV Silicone Sealing: Advantages and Disadvantages
- 4 Gasket Maker Sealing: Advantages and Disadvantages
- 5 Dual-Sealing Approach for Added Security
- 6 Preparing the Surface for Sealant Application
- 7 Applying the Sealant to the Intake Manifold Gasket
- 8 Conclusion
In the intricate world of engine mechanics, there exists a small but mighty component known as the intake manifold gasket. Though often overlooked, this unassuming gasket plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation of your engine. This comprehensive overview will delve into the purpose, importance, and inner workings of the intake manifold gasket, shedding light on its crucial role in optimizing engine performance.
The Purpose and Importance:
At its core, the intake manifold gasket serves one primary purpose: to create a secure seal between the intake manifold and the engine block. By establishing this seal, the gasket effectively prevents any leaks of air or fluids, allowing for an uninterrupted flow of the air-fuel mixture into the combustion chambers. It ensures that your engine receives the precise amount of air and fuel necessary for efficient combustion, directly impacting its overall performance and efficiency.
Materials and Location:
Constructed from durable materials such as rubber, silicone, or metal composite, intake manifold gaskets are designed to withstand the extreme conditions within an engine. These materials possess impressive resilience against high temperatures and pressures generated during operation. Positioned between the intake manifold and the cylinder head atop the engine block, this gasket connects the intake ports to their corresponding cylinders.

Signs of Wear or Damage:
Over time, constant exposure to heat, vibrations, and pressure changes can lead to wear and tear or damage to intake manifold gaskets. It is crucial to remain vigilant for signs such as vacuum leaks, decreased power output, reduced fuel efficiency, and engine misfires. Regular inspection and timely replacement of the gasket are essential for maintaining optimal engine performance.
Sealing Options:

To ensure a reliable seal for your intake manifold gasket, various sealing options are available. One popular choice is RTV silicone sealant, renowned for its flexibility, durability, and resistance to high temperatures. Another option is gasket sealer or gasket maker, which forms a thin film to fill any imperfections on the sealing surfaces. In some cases, a combination of both RTV silicone and gasket sealer may be utilized for enhanced security.
Types of Sealants for Intake Manifold Gaskets
Sealing an intake manifold gasket is vital for the optimal performance of your engine. With various types of sealants available, it’s crucial to choose the right one that suits your needs and specifications. In this article, we will explore different sealants used for sealing intake manifold gaskets, discussing their advantages and disadvantages.
Silicone Sealants:
Silicone sealants are a popular choice due to their ease of application and flexible, durable seal. These sealants can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for intake manifold gaskets. Available in liquid or paste forms, silicone sealants offer versatility for various applications. However, improper application can lead to messy results, so it’s important to carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Gasket Makers:
Gasket makers, also known as form-in-place gaskets (FIPG), are reliable options for sealing intake manifold gaskets. Applied directly onto the gasket or mating surfaces of the engine block and manifold, gasket makers cure quickly to form a solid and flexible seal. They are resistant to oil, fuel, and coolant. However, they may need more frequent replacement compared to other sealants.
Anaerobic Sealants:
Anaerobic sealants are adhesive sealants that cure in the absence of air. Ideal for metal-to-metal joints like intake manifold gaskets, these sealants provide a strong bond that withstands high temperatures and pressures. It’s important to note that anaerobic sealants require proper confinement between surfaces for effective curing.
Compatibility with Gasket Materials:
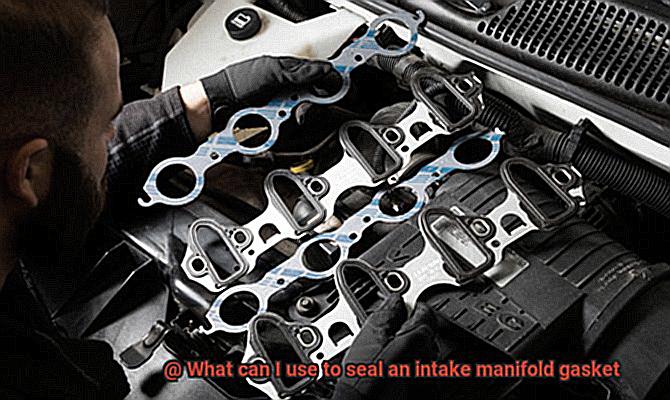

Choosing a sealant that is compatible with the materials used in the intake manifold gasket is crucial. Some sealants may not adhere well to certain gasket materials, resulting in leaks or failures. To ensure the right sealant is chosen for your specific application, consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek professional advice.
Built-in Seals or Coatings:
Modern intake manifold gaskets may come with built-in seals or coatings, eliminating the need for additional sealants. These gaskets are designed to provide a reliable seal without extra products. However, proper installation and torqueing of fasteners should still be ensured to prevent leaks or failures.
RTV Silicone Sealing: Advantages and Disadvantages
RTV silicone sealing, also known as Room Temperature Vulcanizing silicone, is a versatile sealant that offers a multitude of advantages for sealing intake manifold gaskets. It acts as a flexible body armor, protecting your engine’s heart from leaks and maintaining its proper functioning. However, like any warrior, it does have its weaknesses. Let’s dive into the battlefield of RTV silicone sealing and explore its advantages and disadvantages, so you can make an informed choice.
Advantages:
- Heat Resistance: RTV silicone sealing is a true heat warrior, capable of handling extreme temperatures ranging from -60°C to 315°C. It fearlessly protects engine components subjected to intense heat, ensuring their longevity.
- Flexibility: With the agility of a gymnast, RTV silicone sealing can conform to irregular surfaces and create a tight seal. It fearlessly tackles intake manifold gaskets with uneven mating surfaces, leaving no room for leaks.
- Resistance to Vibration: In the face of relentless vibrations and movement, RTV silicone sealing stands strong. Its resilience ensures that the seal remains intact even under the harshest conditions, safeguarding your engine’s performance.
- Fluid Resistance: Like a shield against the onslaught of automotive fluids, RTV silicone sealing provides excellent resistance to oil, gasoline, and other fluids. It bravely prevents leaks and maintains optimal engine functioning.
Disadvantages:
- Curing Time: The time it takes for RTV silicone sealants to fully cure and achieve maximum strength can be a battle against time. With patience as your ally, be prepared to wait several hours for the sealant to reach its full potential.
- Moisture Sensitivity: Moisture during the curing process poses a threat to the bond and effectiveness of the seal. In this battle against moisture, ensure a dry environment during application to guarantee victory.
- Compatibility: While RTV silicone sealing is a fierce opponent to many fluids and chemicals, it may not be compatible with all. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure compatibility with the specific fluids in your application, avoiding any unexpected surprises.
- Surface Preparation: The importance of proper surface preparation should not be underestimated. Before going into battle, make sure the mating surfaces are clean, dry, and free from contaminants or old sealant residue. This ensures optimal adhesion and a reliable seal.
Gasket Maker Sealing: Advantages and Disadvantages
This method employs a silicone-based adhesive or sealant, known as gasket maker, to create a strong and durable bond between two surfaces. While gasket maker sealing offers several advantages, it is crucial to consider its limitations as well. In this article, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of using gasket maker sealing for intake manifold gaskets.
Advantages of Gasket Maker Sealing:
Reliable and Long-lasting Seal:
Gasket makers are renowned for their exceptional adhesive properties, ensuring a secure bond between the intake manifold and the engine block. This eliminates the risk of air or fluid leaks, preventing potential engine damage and maintaining optimal performance.
High Temperature and Chemical Resistance:
Automotive engines generate intense heat, and the intake manifold is exposed to extreme temperatures. Gasket makers are specially formulated to withstand these conditions, making them an ideal choice for sealing intake manifold gaskets. Moreover, they exhibit resistance to oil, coolant, and other chemicals commonly found in engine compartments.
Flexibility in Application:
Unlike pre-cut gaskets, gasket makers offer flexibility in application. They can be easily customized and applied to fill irregularities or gaps in mating surfaces, ensuring a tight and reliable seal. This versatility is particularly useful for sealing intake manifold gaskets with worn or uneven surfaces.
Disadvantages of Gasket Maker Sealing:
Curing Time:
One potential drawback of using gasket maker sealing is the time required for the adhesive to fully cure and achieve maximum strength. Typically, gasket makers require several hours or even overnight curing time before they reach their optimal bonding strength. This can result in longer vehicle downtime during repairs or maintenance.
Compatibility Issues:
Although gasket makers are generally compatible with most metal and rubber surfaces, they may not adhere well to gaskets made of other materials. It is crucial to ensure compatibility between the gasket maker and the specific type of intake manifold gasket being used. In some cases, alternative sealing methods may need to be considered.
Dual-Sealing Approach for Added Security
In the intricate dance of engine mechanics, the intake manifold gasket takes center stage, orchestrating the flow of air and fuel. But what if we could enhance its sealing prowess? Enter the dual-sealing approach – a revolutionary technique that combines two sealing methods or materials to fortify against leaks. In this enlightening article, we will delve into the inner workings of this innovative approach and explore why it has become a game-changer for engine reliability.
Harnessing the Power of Liquid Gasket Sealant:
At the heart of the dual-sealing approach lies the formidable liquid gasket sealant. This remarkable silicone-based solution possesses an almost magical ability to form a flexible and durable seal, capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and harsh chemicals. By applying this sealant to the mating surfaces of the intake manifold and engine block, we create an additional layer of protection against leaks. It expertly fills in any surface imperfections or irregularities, ensuring a tight and impregnable fit that locks out any potential leaks.
Embracing Traditional Gaskets:
The dual-sealing approach also integrates the tried-and-true method of employing traditional gaskets. Acting as a cushion between mating surfaces, these reliable devices provide an initial barrier against leaks. When combined with the liquid gasket sealant, they create an unstoppable duo that offers formidable resistance to leakage.
Unleashing Extra Layers for Unyielding Protection:
In situations where maximum protection is paramount, a single gasket may prove insufficient. Enter additional layers of sealing material as reinforcements. These unsung heroes, known as rubber o-rings, play a pivotal role in certain engine designs by offering an extra layer of safeguarding. Positioned around the intake ports on both the manifold and cylinder head, these tiny yet mighty warriors create an impenetrable seal when compressed between the two mating surfaces. With their unwavering grip, they ensure that leaks remain a distant memory.
Preparation and Maintenance: The Cornerstones of Success:
To unlock the full potential of the dual-sealing approach, meticulous preparation is key. Thoroughly cleansing the mating surfaces and eradicating any remnants of old gasket material or residue is paramount to achieving an effective seal. Additionally, regular inspections and maintenance of the intake manifold gasket are crucial in detecting early signs of leakage or damage. By addressing these issues promptly, we safeguard our engine from further harm and guarantee optimal performance.
Preparing the Surface for Sealant Application
To achieve a strong and long-lasting seal, proper preparation of the surface is essential before applying any sealant. Follow these steps to ensure your surface is ready to go:
Step 1: Thoroughly clean the surface.
Dirt, grease, and residue can hinder the adhesion of the sealant. Use a degreaser or solvent safe for engine components to remove any contaminants. Take a lint-free cloth or paper towel and wipe away all the grime. A clean surface is crucial for optimal adhesion.
Step 2: Inspect and repair.
Play detective and closely examine the surface for cracks, nicks, or pitting that could compromise the seal. Address any issues before applying the sealant. Fill small cracks and imperfections with an appropriate filler or epoxy, then sand them down for a smooth finish.
Step 3: Create a rough texture.
Enhance sealant adhesion by gently sanding the surface with fine-grit sandpaper. Use a light touch in a circular motion to avoid damaging the surface. The goal is to create a rough texture that promotes better bonding.
Step 4: Clean again.
After sanding, clean away any debris or dust generated during the process. Give the surface one final wipe-down with a lint-free cloth or paper towel. We want it squeaky clean.
Step 5: Apply primer.
Before applying the sealant, give your surface some primer love. A primer or adhesion promoter enhances the bond between the sealant and the surface, ensuring a better seal. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application and drying times.
Step 6: Time to seal the deal.
Now it’s finally time to apply the sealant. Choose a sealant specifically designed for your application, such as intake manifold gaskets. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application techniques and curing times. Apply a thin and even layer, ensuring complete coverage of the gasket area.
Step 7: Patience is key.
After applying the sealant, allow it to cure fully before assembling the parts. Curing times can vary, so refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Double-check that your sealant is compatible with the gasket material to avoid any compatibility issues.
Applying the Sealant to the Intake Manifold Gasket
If you’re dealing with leaks in your intake manifold, fear not. We have the solution for you. Let’s dive into the process of applying sealant to an intake manifold gasket step by step, ensuring a perfect seal and putting an end to those frustrating leaks.
To start, gather the necessary tools and materials. You’ll need a high-quality sealant specifically designed for intake manifold gaskets. Don’t settle for regular adhesives or sealants that won’t hold up against the intense heat and pressure the gasket faces.
Before applying the sealant, it’s essential to thoroughly clean the surfaces. Use a degreaser or solvent to remove any oil, dirt, or debris from both the intake manifold and engine block surfaces. A clean surface is key to achieving proper adhesion of the sealant.
Now it’s time to apply the sealant. Begin by adding a thin, even layer of sealant onto the intake manifold gasket. Avoid going overboard with the sealant – too much can squeeze out and cause more leaks. A thin layer is sufficient for creating a secure seal without excessive buildup.
Use a brush or your fingertip to spread the sealant evenly across the entire surface of the gasket. Make sure to cover every area, including the bolt holes and corners. Take your time during this step and be meticulous to ensure complete coverage.
With the sealant applied, carefully position the intake manifold onto the engine block. Align it with the bolt holes and gently press it down to establish a firm connection between the two surfaces. Take care not to disturb or smear the sealant as you do so.
Once in place, gradually tighten the bolts in a crisscross pattern, distributing pressure evenly and ensuring a secure fit. Refer to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications for tightening the bolts – we don’t want any loose ends.
After tightening the bolts, allow the sealant to cure according to its instructions. This typically involves leaving it undisturbed for a specified amount of time, often overnight or several hours. During this curing period, avoid subjecting the sealant to extreme temperatures or pressures by refraining from starting the engine.
Once the sealant has properly cured, double-check the tightness of the bolts to ensure they remain properly torqued. This step is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the sealant and preventing future leaks.
And there you have it – a perfectly sealed intake manifold gasket. By using the appropriate sealant, thoroughly cleaning the surfaces, and applying a thin, even layer of sealant, you can bid farewell to those annoying leaks.
BykeFgsAyIg” >
Conclusion
When it comes to sealing an intake manifold gasket, there are a few options you can consider.
One popular choice is using a high-quality silicone gasket sealant. This versatile adhesive forms a strong bond and creates a tight seal that can withstand the heat and pressure of your engine.
Another option is using an anaerobic sealer, which is specifically designed for sealing metal surfaces. This type of sealer cures in the absence of air, creating a durable and reliable seal.
Additionally, some people opt for using gasket maker or RTV silicone as an alternative solution. These products are known for their flexibility and ability to fill gaps effectively.
Remember, a properly sealed intake manifold gasket is crucial for maintaining the performance and efficiency of your engine.






