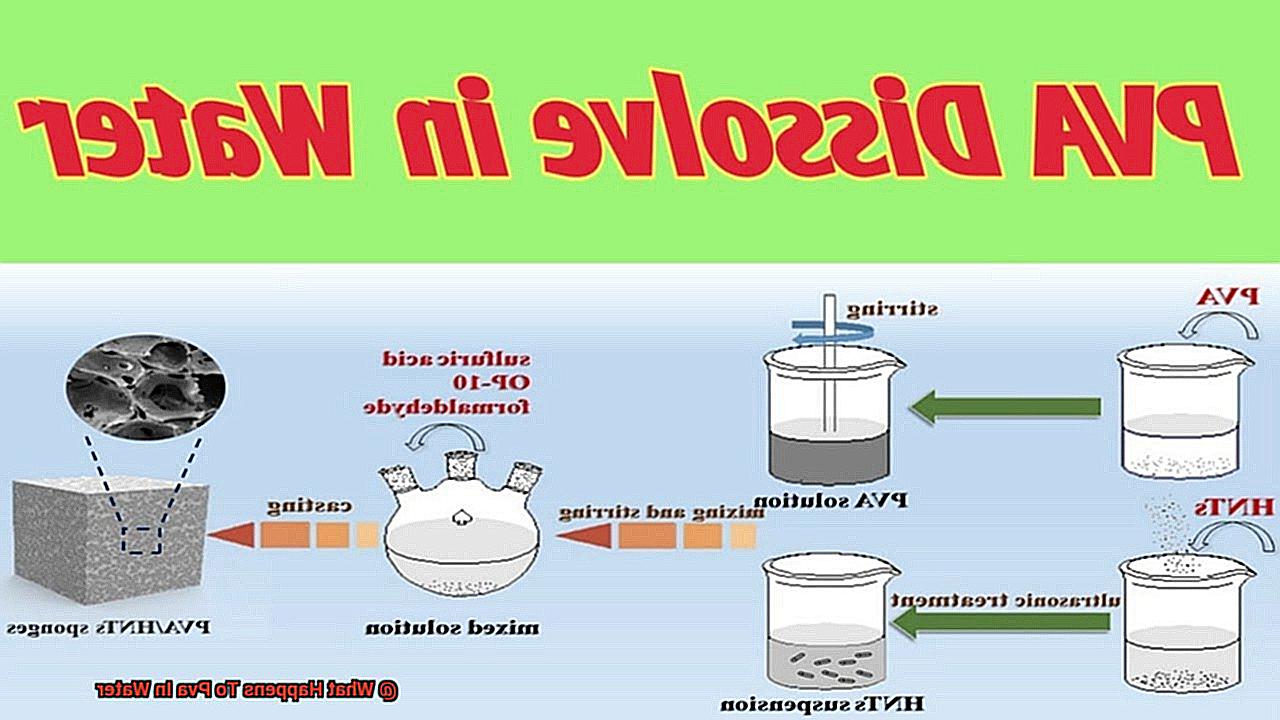
Do you ever ponder what happens when Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) meets water? Are you curious to know how this adaptable polymer behaves under different conditions? Well, buckle up and get ready to dive into the captivating world of PVA and water chemistry.
PVA is a synthetic resin that finds its use in various industrial and household applications. Its distinct features make it an exceptional adhesive, emulsifier, and coating agent. However, being water-soluble, PVA dissolves effortlessly in water. But does it disappear entirely or transform into something else after dissolving?
In this blog post, we will explore the science behind PVA and water interaction. We will scrutinize what happens to PVA in different water environments such as hot and cold water, acidic and alkaline solutions, and under varying levels of salinity. Moreover, we will take a closer look at the factors that influence the solubility of PVA in water – including molecular weight, temperature, and concentration.
So if you’re eager to unravel the mysteries of PVA’s behavior in water – stick around. Get set for an exciting journey into the world of polymer chemistry.
What is PVA?
Contents
PVA, or polyvinyl acetate, is a synthetic polymer that has been in use for over a century. It’s commonly used in the manufacturing of adhesives, coatings, and films for everything from woodworking to paper crafts to household repairs.
What makes PVA so great? For starters, its water-soluble properties make it an ideal adhesive. When wet, PVA becomes sticky and can bond to just about any surface. Plus, it dries clear and doesn’t leave any residue behind, making it perfect for use in arts and crafts projects where appearance is key.
But PVA’s versatility doesn’t end there. It can also be applied as a protective coating to surfaces like wood and metal. The thin film it creates helps protect against moisture and other environmental factors, keeping your surfaces looking their best.
Of course, prolonged exposure to water can cause PVA to break down and lose its adhesive properties. But fear not – by adding certain additives or cross-linking agents to its formulation, PVA can be made more water-resistant and suitable for use in damp or humid conditions.
How Does PVA React to Water?
PVA, or polyvinyl acetate, is a popular adhesive that has been used for various projects for over a century. It’s renowned for its versatility, strength, and ability to dry clear without leaving any residue. However, how does it react to water?
Upon exposure to water, PVA glue initially softens and then swells. The extent of swelling depends on the concentration of PVA in the adhesive and the temperature of the water. As the PVA absorbs water, it becomes more flexible and loses some strength. But don’t worry – once the water evaporates, the glue regains its original properties.
It’s important to note that not all types of PVA are created equal. Some formulations are designed to be more water-resistant than others. For example, there are PVA glues specifically labeled as “water-resistant” or “waterproof.” These types of glues contain additional ingredients that make them more resistant to moisture.

In general, PVA glue is not recommended for use in situations where it will be exposed to frequent or prolonged contact with water. For example, it may not be suitable for outdoor projects or items consistently exposed to humidity. However, for numerous applications, PVA glue is an excellent choice due to its strength, versatility, and ease of use.
Factors That Affect the Solubility of PVA in Water
One of the most critical factors is the degree of hydrolysis. Hydrophilic properties increase as the degree of hydrolysis rises, making PVA more readily soluble in water.
Molecular weight is another factor that affects PVA solubility. Long polymer chains in high molecular weight PVA require more energy to dissolve in water, making low molecular weight PVA more soluble than high molecular weight PVA.
Temperature also plays a role in PVA solubility. Increasing temperatures increase kinetic energy, making molecules more likely to dissolve, thus increasing the solubility of PVA in water.
In addition to temperature, pH levels can affect PVA solubility. Neutral or slightly alkaline conditions promote optimal solubility, while acidic solutions can cause PVA hydrolysis, leading to insoluble PVAc formation.
Lastly, adding salt to a solution can decrease the availability of water molecules for dissolving PVA, as salt ions compete with PVA for water molecules.
How Water Can Weaken the Adhesive Properties of PVA
Polyvinyl acetate, or PVA, is a popular water-based adhesive used in woodworking and crafting projects. However, this versatile glue can lose its adhesive properties when it comes into contact with water. In this blog post, we will delve into how water weakens the adhesive properties of PVA and how to prevent it from happening.
PVA glue consists of long polymer chains that are held together by weak hydrogen bonds. When water is introduced to PVA, it disrupts these hydrogen bonds, causing the polymer chains to separate from each other. This results in a weaker bond between the glue and the surface it was applied to. Hence, you may notice that your project loses its grip when exposed to water.
Another way in which water can weaken PVA is through swelling. When PVA glue is exposed to water, it absorbs the water and swells up. This can cause the glue to lose its grip on the surface it was applied to as the swelling pushes the glue away from the surface.
It’s essential to note that not all PVAs are created equal in terms of their resistance to water. Some PVAs are specially formulated for use in wet environments and have higher levels of water resistance than others. These types of PVAs contain additives that help strengthen the bond between the glue and the surface, even when exposed to water.
To minimize exposure to water, store your PVA in a dry location and avoid using it in damp or humid environments. Additionally, you can choose a PVA with higher levels of water resistance for projects that may come into contact with moisture.
Making PVA More Water-Resistant
There are several methods you can use to make your PVA glue more water-resistant and durable.
One common approach is to mix your PVA glue with a waterproofing agent like silicone. By doing this, you create a stronger bond that resists water penetration and ensures better long-term performance. Another effective method is to apply a clear varnish or epoxy coating over the dried PVA glue. This extra layer of protection helps safeguard your glue from water damage and prolongs its lifespan.
It’s worth noting, however, that these methods may alter the adhesive strength and properties of your PVA glue. Therefore, it’s strongly recommended to test the glue before using it for any critical projects.
Another crucial consideration when making PVA glue more water-resistant is the surface on which you’re applying it. Depending on the material, such as wood or metal, additional preparation or priming may be necessary to ensure optimal adhesion and water-resistance.
Swtv8Acu9P8″ >
Conclusion
In summary, Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) is a jack-of-all-trades polymer that has many uses in both industrial and household settings. Its water-soluble nature makes it an excellent adhesive, emulsifier, and coating agent. However, when exposed to water for extended periods of time, PVA can deteriorate and lose its adhesive properties. The degree of swelling depends on the concentration of PVA in the glue and the temperature of the water.
The solubility of PVA in water is influenced by several factors, including molecular weight, temperature, pH levels, and salinity. When salt is added to a solution, it can reduce the amount of available water molecules for dissolving PVA.
Water weakens PVA’s adhesive strength by disrupting hydrogen bonds between long polymer chains and causing them to separate from each other. Swelling can also push the glue away from the surface it was applied to.
To make PVA more resistant to water damage, you can mix it with a waterproofing agent like silicone or apply a clear varnish or epoxy coating over the dried glue. However, it’s important to note that these methods may alter the adhesive strength and properties of your PVA glue.
Overall, understanding how PVA behaves in water is critical for optimizing its performance in various applications.