When it comes to healing wounds, closing them up is a big deal.
Doctors and surgeons have always relied on stitches and sutures to bring the skin back together, but there’s a new adhesive in town that’s causing quite a stir. It’s like magic glue that can seal up wounds without any invasive procedures.
This incredible stuff is called medical adhesive or tissue glue, and it’s changing the game for doctors everywhere. In this blog post, we’ll take a deep dive into this amazing product, exploring what it’s made of, how it’s used, and why it’s become an absolute must-have for medical pros.
So if you’ve ever wondered about the glue doctors use to close up wounds, get ready for some mind-blowing info.
What is Cyanoacrylate Glue?
Contents
- 1 What is Cyanoacrylate Glue?
- 2 Types of Cyanoacrylate Glue
- 3 Advantages of Using Cyanoacrylate Glue for Wound Closure
- 4 Disadvantages of Using Cyanoacrylate Glue for Wound Closure
- 5 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Type of Glue for Wound Closure
- 6 How to Properly Apply Cyanoacrylate Glue for Wound Closure
- 7 Potential Complications from the Use of Cyanoacrylate Glue on Wounds
- 8 Alternatives to Using Cyanoacrylate Glue for Wound Closure
- 9 Conclusion
In the fast-paced world of medicine, innovation is crucial. And when it comes to wound closure, cyanoacrylate glue has revolutionized traditional methods. Known as super glue or crazy glue, this fast-acting adhesive has found its place in the medical field. Let’s delve into the wonders of cyanoacrylate glue and its applications in medicine.
The Power of Cyanoacrylate Glue:
Cyanoacrylate glue is a clear liquid that hardens swiftly upon contact with moisture, creating a strong bond. Its unique properties make it an ideal choice for wound closure, offering advantages over traditional methods. With its rapid application time, reduced scarring, and lower risk of infection, cyanoacrylate glue has become a game-changer in the medical world.
Medical Applications:
Cyanoacrylate glue serves as an alternative to sutures or stitches for specific wound closures in the medical field. It simplifies the process by eliminating the need for anesthesia and enables faster wound closure. The adhesive is carefully applied along the wound edges, polymerizing rapidly upon contact with moisture. This creates a protective barrier that holds the wound together while it heals naturally.
Benefits and Considerations:
The benefits of cyanoacrylate glue are numerous. Its fast-acting nature allows for quick wound closure, minimizing patient discomfort and reducing overall procedure time. Additionally, its strong bonding capabilities provide reliable support during the healing process, leading to reduced scarring. Moreover, since cyanoacrylate glue forms a barrier, it lowers the risk of infection.
However, it’s essential to consider certain factors before opting for cyanoacrylate glue closure. Wound size, location, and patient health must be taken into account. Deep wounds or those involving vital structures may require traditional sutures or alternative closure techniques.
Types of Cyanoacrylate Glue

It’s called cyanoacrylate glue, and it’s not your ordinary glue. This super glue is specially designed for medical use, and it works like magic to seal wounds and promote faster healing. Let’s explore the different types of cyanoacrylate glues that doctors use for wound closure and how they work their magic.
Ethyl Cyanoacrylate: The Speedy Healer
When it comes to small superficial wounds, ethyl cyanoacrylate glue is the go-to choice for doctors. This clear glue dries quickly, forming a strong bond between the wound edges. Its flexibility allows for natural movement without the risk of tearing or reopening the wound. It’s like having a protective shield that promotes faster healing without any discomfort.
Butyl Cyanoacrylate: The Supporter
For deeper wounds or areas that experience frequent movement, doctors opt for butyl cyanoacrylate glue. Similar to ethyl cyanoacrylate, it forms a strong bond between the wound edges. However, it has a slightly longer drying time and provides excellent tensile strength, offering the support and tension resistance needed for proper healing.
Medical-Grade Cyanoacrylate Glues: Safe and Sterile
In addition to ethyl and butyl cyanoacrylate glues, doctors also have access to medical-grade cyanoacrylate glues. These glues are specially formulated and undergo rigorous testing to ensure their safety and effectiveness in wound closure. They are biocompatible, meaning they won’t cause any harm or adverse reactions in the body. Plus, they come in sterile applicators designed for easy and precise application.
Conclusion:
Cyanoacrylate glues, like ethyl and butyl cyanoacrylate, are doctors’ secret weapons for healing wounds. They provide a quick and effective way to close wounds, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection. Medical-grade cyanoacrylate glues take it a step further by ensuring safety and sterility. However, it’s important to remember that not all wounds can be closed with glue alone.
Doctors will assess each case individually to determine the most appropriate closure method. So the next time you see a doctor using “super glue,” you’ll know the magical powers it holds in healing wounds.
Revised Research:
Cyanoacrylate glue, commonly known as “super glue,” is a type of adhesive that is commonly used by doctors to close wounds. This glue is highly effective in sealing the edges of a wound together, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection. There are different types of cyanoacrylate glues that doctors can choose from, depending on the specific needs of the wound.
Advantages of Using Cyanoacrylate Glue for Wound Closure
When it comes to wound closure, the traditional methods of sutures and staples are being challenged by the magical powers of cyanoacrylate glue. This liquid adhesive offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive option for both patients and healthcare professionals. In this blog post, we will explore the key advantages of using cyanoacrylate glue for wound closure and why it is gaining popularity in the medical field.
Advantage 1: Quick and easy application
Cyanoacrylate glue offers a revolutionary way to close wounds without the need for stitches or staples. This adhesive is applied directly to the wound, forming an instant bond upon contact with moisture. The quick application saves time in the procedure room and eliminates the discomfort associated with traditional methods.
Advantage 2: Minimal scarring
One of the greatest benefits of using cyanoacrylate glue is its ability to minimize scarring. The glue creates a thin film over the wound, acting as a protective barrier against infections while promoting optimal healing conditions. Unlike sutures or staples that can leave noticeable marks, cyanoacrylate glue offers a cosmetically appealing alternative.
Advantage 3: Enhanced wound healing
By acting as a “second skin,” cyanoacrylate glue holds the edges of the wound together, providing stability and support. This reduces tension and prevents tissue separation, leading to faster healing and reduced risk of complications such as wound reopening. Additionally, the breathable nature of this adhesive allows oxygen to reach the wound and promote the healing process.
Advantage 4: Reduced pain and discomfort
The application and removal of sutures or staples can be painful and uncomfortable for patients. However, cyanoacrylate glue eliminates this issue. It is applied directly to the wound surface without any physical manipulation of the skin, resulting in minimal discomfort. Furthermore, there are no sutures or staples to be removed, reducing pain and anxiety during the healing process.
Advantage 5: Lower risk of infection
Cyanoacrylate glue creates a protective barrier over the wound, sealing it off from bacteria and other pathogens. This significantly reduces the risk of infection and contributes to better wound management and improved patient outcomes. The adhesive properties of cyanoacrylate glue ensure a tight closure, leaving no gaps or spaces for bacteria to thrive.
Disadvantages of Using Cyanoacrylate Glue for Wound Closure
Cyanoacrylate glue, known as “super glue,” has become popular for wound closure due to its convenience and effectiveness. However, it is important to consider the drawbacks associated with using this adhesive in medical settings. This article explores the disadvantages of using cyanoacrylate glue for wound closure and highlights key concerns that should be taken into account.
Allergic Reactions:
One major drawback of cyanoacrylate glue is the potential for allergic reactions. Although rare, some individuals may develop redness, itching, swelling, and even blisters at the site of application. Proper allergy testing is crucial before using this adhesive.
Tissue Damage:
Another concern with cyanoacrylate glue is the risk of tissue damage. Contact with healthy skin during application can cause burns or irritation, leading to delayed healing and complications. Precise technique is essential to avoid such damage.
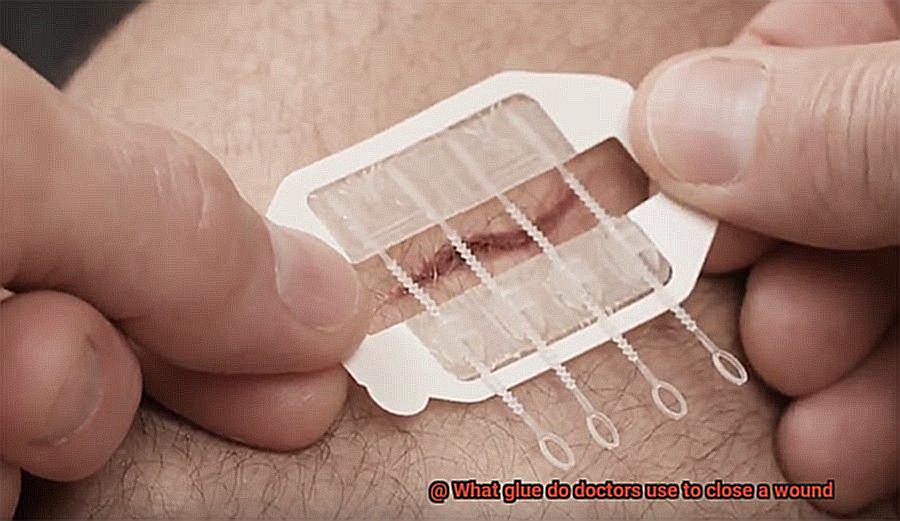

Unsuitability for Complex Wounds:
Cyanoacrylate glue is not suitable for deep, complex, or contaminated wounds. It may not effectively seal these types of wounds, increasing the risk of infection or other complications. Traditional methods like sutures or staples may be more appropriate.
Limited Wound Assessment:
Unlike sutures or staples that allow easy monitoring of wound healing progress, cyanoacrylate glue creates a barrier that hinders assessment for signs of infection or other issues requiring medical attention. Timely intervention may be compromised.
Cosmetic Outcomes:
While cyanoacrylate glue provides a strong bond, it may not result in aesthetically pleasing closures compared to other methods. This is particularly concerning for wounds in visible areas like the face or hands. Location and cosmetic impact should be carefully considered.
Cost Considerations:
The cost of cyanoacrylate glue can be a disadvantage, especially compared to traditional methods like sutures or staples. It is generally more expensive, which may pose challenges for individuals without insurance or in resource-limited settings.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Type of Glue for Wound Closure
When it comes to choosing a type of glue for wound closure, healthcare professionals have an important decision to make. With a plethora of options available, it can be overwhelming to determine which glue is the best choice. In this article, we will delve into the various factors that should be considered when selecting a type of glue for wound closure.
First and foremost, biocompatibility is crucial. The chosen glue must be more than just a sticky substance; it needs to be non-toxic and non-irritating to the surrounding tissues. It should not cause any adverse reactions or allergies in the patient. This ensures that the healing process is not hindered by any negative side effects.
In addition to biocompatibility, strength and flexibility are key factors to consider. The glue used for wound closure should possess enough strength to securely hold the wound edges together, promoting proper healing. At the same time, it must also be flexible enough to allow for natural movement of the skin without causing tension or stress on the wound.
Adhesion properties are another important consideration. The glue should have remarkable adhesive properties, capable of adhering well to both dry and moist surfaces. This allows for the creation of a watertight seal, preventing infection and promoting healing.
Drying time is a factor that cannot be overlooked. The glue should dry quickly to minimize the risk of contamination, but it also needs to allow enough time for proper positioning and alignment of the wound edges before it sets. Finding the right balance is key.
Transparency is preferred in glues used for wound closure as it allows for easy monitoring of the wound site without frequent dressing changes. This is especially important in cosmetically sensitive areas where aesthetics play a significant role.
Ease of use and availability are practical factors that should not be neglected. The chosen glue should come in user-friendly packaging with clear instructions for proper application. Additionally, it needs to be readily available, ensuring timely wound closure and preventing treatment delays.
Lastly, while not the primary factor, cost is a consideration that healthcare facilities need to take into account. They must consider the cost-effectiveness of the glue, including factors such as its shelf life, storage requirements, and frequency of use.
How to Properly Apply Cyanoacrylate Glue for Wound Closure
Well, they have a super cool glue called cyanoacrylate glue, also known as surgical glue or medical adhesive. This special glue acts like magic, sealing wounds and helping them heal faster. Today, we’re going to learn how to properly apply cyanoacrylate glue for wound closure, just like the doctors do.
Step 1: Clean the Cut
Before applying the glue, it is crucial to clean the cut thoroughly. Doctors use a special solution called an antiseptic to clean the wound and remove any dirt or germs. This ensures that the wound is nice and clean, creating an optimal environment for the glue to work its magic.
Step 2: Bring the Edges Together
Next, it’s time to bring the edges of the cut together, just like piecing together a puzzle. Using sterile forceps or gloved fingers, doctors gently press the edges of the wound together. It’s important to ensure that everything is perfectly aligned, with no tension or gaps between the edges. This step sets the foundation for a successful glue application.
Step 3: Apply the Glue
Now comes the fun part – applying the glue. Doctors use a tiny brush or a special applicator to apply a thin layer of cyanoacrylate glue along the cut. It’s like drawing a rainbow with glue. The key here is to apply the glue in a continuous line, ensuring it covers the entire length of the wound. This even distribution promotes proper adhesion and healing.
Step 4: Let It Dry
After applying the glue, we have to be patient and let it dry. Just like waiting for your watercolor painting to dry before touching it, we need to give the glue time to set. Doctors gently press on the wound with sterile gauze or use special bandages to hold everything in place while the glue dries. This ensures that the wound edges stay together, allowing the glue to work its magic.
Step 5: Protect and Care for the Wound
Once the glue is dry, it forms a protective seal over the wound. This seal helps keep out harmful germs and bacteria, allowing the wound to heal faster. To ensure proper healing, it’s important to keep the wound clean and dry. Avoid getting it wet for at least a day after applying the glue. This will give the glue enough time to bond securely and support the healing process.
Potential Complications from the Use of Cyanoacrylate Glue on Wounds
Cyanoacrylate glue, commonly known as “super glue,” has gained popularity as an alternative to traditional sutures or staples for wound closure. However, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential complications that can arise from using this adhesive on wounds.
One significant complication is allergic reactions. Some individuals may have a hypersensitivity or allergy to the components of cyanoacrylate glue, leading to redness, itching, swelling, and even blistering or ulceration around the wound site. In severe cases, immediate medical attention may be necessary. It is essential to inform healthcare professionals about any known allergies before they apply cyanoacrylate glue to a wound.
Another potential complication is poor wound healing. While cyanoacrylate glue can work well for certain wounds, it may not be suitable for all cases. If the wound is deep, contaminated, or at high risk of infection, using cyanoacrylate glue might hinder proper healing. In such situations, traditional sutures or staples may be a better option.
Improper alignment of wound edges or tension on the wound site can result in poor wound approximation and increased scarring when using cyanoacrylate glue. Healthcare professionals must carefully assess the type and location of the wound before deciding on this method. Factors such as the patient’s overall health and the likelihood of complications should be considered.
Pain or discomfort can also occur when cyanoacrylate glue is used to close a wound, especially if it comes into contact with nerve endings or sensitive tissues around the site. Healthcare professionals should inform patients about potential discomfort and ensure adequate pain management measures are in place.
Lastly, there is a risk of accidental contact with sensitive areas like eyes or mouth if the glue is not applied with caution. Healthcare professionals must take proper precautions and follow established protocols to prevent any mishaps.
Alternatives to Using Cyanoacrylate Glue for Wound Closure
In the world of wound closure, cyanoacrylate glue, also known as “super glue,” has long been the go-to option. Its fast-drying and adhesive properties have made it a favorite among medical professionals. However, there are instances where alternative options may be desired or necessary. So, let’s take a journey into the realm of wound closure alternatives that offer unique benefits and considerations.
Medical Adhesive Tapes:
Versatility meets convenience with medical adhesive tapes. Crafted from hypoallergenic materials, these tapes provide a secure closure for small wounds. They shine in areas where using glue may prove challenging, such as joints or areas with excessive movement. Applying and removing medical adhesive tapes is a breeze, making them an ideal choice for wound closure.
Sutures or Stitches:
For larger or deeper wounds, sutures or stitches often take center stage. These time-honored heroes require skill and precision but offer better control over wound edges and allow for precise alignment during the healing process. They are commonly employed when there is a higher risk of infection or when cosmetic outcomes are paramount. Sutures represent a tried-and-true method for wound closure that healthcare professionals have relied on for decades.
Staplers:
Enter surgical staplers, the swift warriors of wound closure. With their quick and efficient manner, they excel at closing wounds with straight edges or well-defined margins. While frequently seen in operating rooms, specialized staplers designed for wound closure have emerged in emergency departments and outpatient settings. Staplers provide a reliable option that ensures the wound edges remain securely held together.
Adhesive Strips (Butterfly Closures):
Adhesive strips, affectionately known as butterfly closures or Steri-Strips, offer an elegant alternative to cyanoacrylate glue. These strips gracefully bridge the gap across the wound, holding the edges together with gentle strength. They shine brightest when it comes to small cuts or lacerations that do not require deep closure. Applying adhesive strips is a breeze, and they can be left in place until they naturally fall off.
Tissue Adhesives:
Prepare to be amazed by the wonders of tissue adhesives made from fibrin or collagen. These adhesives mimic the body’s natural clotting process and promote wound healing. When applied directly to the wound surface, they forge a robust bond between the edges. Tissue adhesives often take center stage in delicate areas like the face or when there is a risk of scarring.
Conclusion
In conclusion, doctors use a special type of glue called tissue adhesive to close wounds.
This remarkable adhesive is specifically designed for medical purposes and provides a secure and effective way to seal cuts and incisions. With its quick-drying properties, tissue adhesive forms a strong bond that holds the edges of the wound together, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection.
This innovative glue is an excellent alternative to traditional sutures or staples, offering patients a more comfortable and cosmetically pleasing closure method.