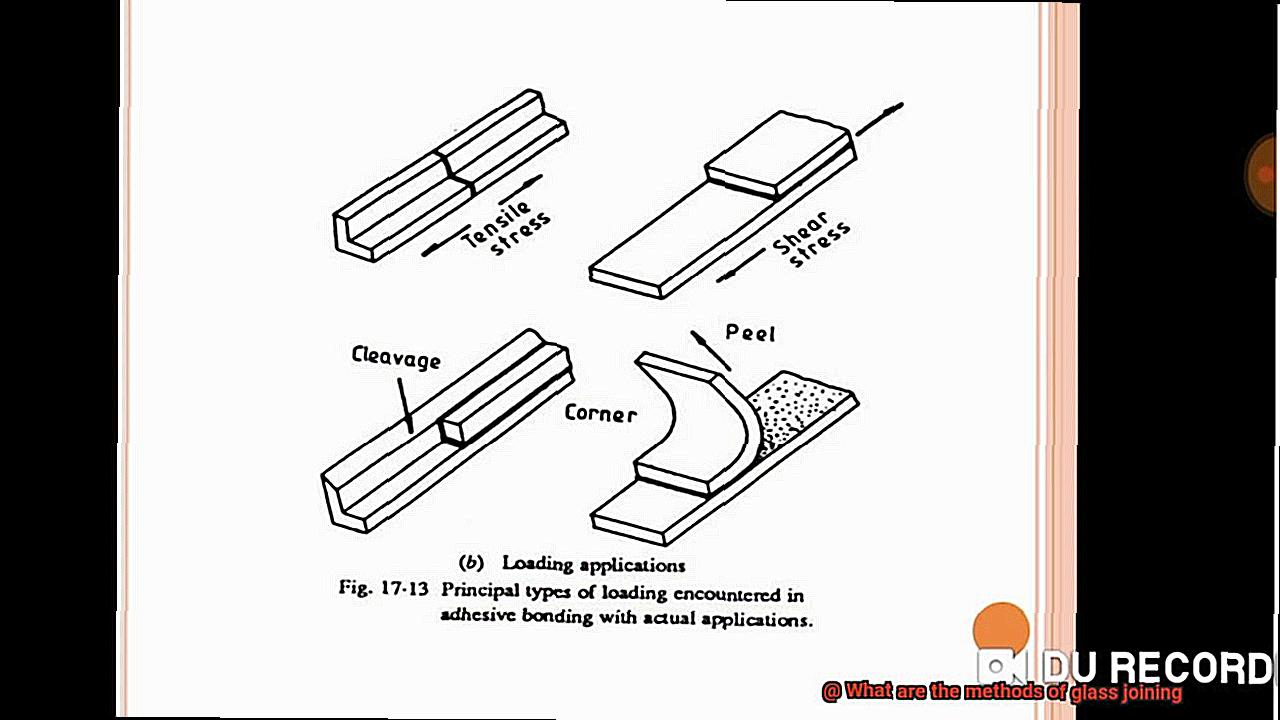
It’s in our windows, our mirrors, and those beautiful glass masterpieces. But how do they stick all those pieces together?
Well, my friend, there’s more than one way to join glass. In this blog post, we’re going to dive into the fascinating world of glass joining methods.
We’ll explore adhesive bonding, mechanical fastening, and thermal joining. Whether you’re a glass lover or just curious about the magic behind it all, get ready for a wild ride through the world of glasswork.
Let’s jump in and uncover the secrets of glass joining together.
Adhesive Bonding: Overview and Benefits
Contents
- 1 Adhesive Bonding: Overview and Benefits
- 2 Thermal Joining: Overview and Benefits
- 3 Welding: Overview and Benefits
- 4 Laser Welding: Overview and Benefits
- 5 Mechanical Methods of Joining Glass: Overview and Benefits
- 6 Ultrasonic Welding: Overview and Benefits
- 7 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Method for Joining Glass
- 8 Conclusion
Adhesive bonding, a versatile and effective method of joining glass, offers numerous benefits that make it a preferred choice in various industries. Let’s delve into the overview and advantages of adhesive bonding for joining glass.
Firstly, adhesive bonding creates a strong and durable bond by evenly distributing stress across the entire bonded area. This reduces the risk of stress concentrations that can lead to cracks or fractures, ensuring the longevity and integrity of the bond.
Secondly, adhesive bonding is highly versatile, capable of joining different types of glass such as tempered glass, laminated glass, and specialty glasses like borosilicate or quartz glass. With a wide range of adhesive formulations available, customization is possible to meet specific application requirements. Whether it’s high temperatures, extreme weather conditions, or exposure to chemicals, there’s an adhesive that can withstand it.
Thirdly, adhesive bonding offers aesthetic advantages by creating a seamless and clean appearance without visible fasteners or welding marks. This is crucial in applications where aesthetics play a significant role, such as architectural glass installations or automotive windshields.
Furthermore, adhesive bonding provides enhanced resistance against vibrations and shocks. Acting as a cushioning material, the adhesive absorbs energy and reduces the transmission of vibrations between bonded glass surfaces. This makes it ideal for applications that require impact resistance, like aircraft windows or electronic displays.
Lastly, adhesive bonding excels in sealing capabilities. It forms a tight seal between joined glass surfaces, preventing the ingress of moisture, dust, or other contaminants. This is essential in applications where maintaining a sealed environment is critical, such as laboratory equipment or medical devices.
Thermal Joining: Overview and Benefits
Thermal joining is a versatile and widely used method for joining glass pieces together. Through the application of heat, this technique creates strong and durable bonds between glass pieces, making it suitable for various industries and applications.
There are different sub-methods of thermal joining, including welding, fusing, and annealing. Welding involves heating the glass pieces until they reach their melting point and then pressing them together to form a bond. It is commonly used for joining large glass pieces or creating complex shapes.
Fusing, on the other hand, involves heating the glass pieces until they soften and fuse together. Unlike welding, fusing does not require the glass to reach its melting point. This technique is often used for creating decorative glass objects or joining smaller glass pieces together.
Annealing is an essential step in any thermal joining process. It involves heating the glass to a specific temperature and then slowly cooling it to relieve internal stresses. This helps strengthen the glass and prevent cracking or breaking during thermal joining.
One of the key benefits of thermal joining is its ability to create seamless joints with minimal visible traces. When done correctly, thermal joining can result in joints that are as strong as the glass itself, providing a clean and aesthetically pleasing finish.
Another advantage is the versatility of thermal joining. It can be used to join different types of glass, such as soda-lime glass, borosilicate glass, or tempered glass. This makes it suitable for a wide range of applications in industries like automotive, construction, and electronics.
Furthermore, thermal joining offers the advantage of being a relatively fast and efficient method. Depending on the size and complexity of the glass pieces being joined, the entire process can be completed within a short period. This makes it a cost-effective choice for manufacturers who require high production rates.
Welding: Overview and Benefits
Welding, the process of joining glass by heating it to its melting point and fusing it together, offers numerous benefits in various applications.
- Strength: Welding creates a seamless joint between glass pieces, resulting in a connection as strong as the glass itself. This makes it suitable for structural components or load-bearing elements.
- Versatility: Welding can join different types of glass, including soda-lime, borosilicate, and specialty glasses like quartz or tempered glass. This flexibility allows for a wide range of applications from small crafts to large-scale industrial constructions.
- Precision and control: Welding offers excellent precision by directing heat precisely to the desired area. This ensures that only the necessary portions of the glass are melted and fused together, crucial for delicate or intricate glass pieces.
- Joining with other materials: Welding allows for the joining of glass to metals, ceramics, or other types of glass. This opens up possibilities for creating complex structures that combine different materials.
- Aesthetics: When done correctly, welding can result in a nearly invisible joint with minimal visible seams or marks on the surface of the glass. This makes it appealing for applications where aesthetics are important, such as art installations or architectural designs.
- Durability: Welded joints are resistant to temperature changes, moisture, and other environmental factors that can weaken or degrade other types of bonds. This makes welding a reliable choice for applications requiring durability and longevity.
Laser Welding: Overview and Benefits
Laser welding, a highly advanced and precise method of joining glass components, has become increasingly popular in various industries due to its numerous benefits and advantages.
Firstly, laser welding offers clean and precise welds. The laser beam can be focused to a very small spot size, allowing for intricate and detailed welds. This is particularly advantageous when working with delicate glass components or complex designs. The precision offered by laser welding ensures minimal distortion or damage to the surrounding areas, resulting in high-quality and visually appealing welds.
Additionally, laser welding provides excellent control over the heat input during the joining process. The laser beam can be precisely controlled in terms of power, duration, and intensity, allowing for accurate heat affected zone control. This is crucial when working with glass, as excessive heat can lead to thermal stress and cracking. Laser welding minimizes these risks by providing precise control over the heat input, ensuring that the glass components are joined without causing any damage.
Another notable benefit of laser welding is its quick processing time. The high-energy laser beam can rapidly melt and fuse the glass surfaces together, resulting in fast and efficient joining. This time-saving advantage is especially valuable in industries where production efficiency is crucial. With laser welding, manufacturers can significantly reduce the assembly time required for joining glass components, leading to increased productivity and cost savings.
Furthermore, laser welding is a non-contact joining method, eliminating the risk of contamination or damage that can occur with traditional methods involving mechanical tools or adhesives. Laser welding ensures a clean and hygienic joining process, making it ideal for applications in industries such as medical devices or food processing, where cleanliness and sterility are paramount.
Lastly, laser-welded joints offer excellent strength and durability. The high-energy laser beam creates a strong bond between the glass surfaces, resulting in welds that can withstand mechanical stresses and environmental conditions. This makes laser-welded glass components highly reliable and long-lasting, suitable for demanding applications where structural integrity is essential.
Mechanical Methods of Joining Glass: Overview and Benefits
Mechanical methods of joining glass offer a multitude of benefits compared to other joining methods like gluing or welding. These methods provide strong and durable connections, making them ideal for applications where strength and stability are crucial, such as in architectural structures or automotive components. Mechanical joints can withstand significant weight and pressure without compromising their integrity.
In addition to their durability and strength, mechanical methods of joining glass also offer versatility. They can be used with different types of glass, including tempered, laminated, or curved glass. This allows for flexibility in design and construction, as they can be applied to various shapes and sizes of glass pieces.
One of the advantages of mechanical joints is their easy disassembly and reassembly. In case repairs or modifications are needed, the joints can be easily undone without causing damage to the glass pieces. This provides greater flexibility and cost-effectiveness in maintenance or remodeling projects.
Furthermore, some mechanical methods, like laser welding, create visually appealing welds that are as beautiful as a work of art. This makes them suitable for applications where aesthetics are important.
In terms of practical benefits, mechanical methods offer controlled heat input, particularly with laser welding. This minimizes thermal stress and the risk of cracking in the glass components, ensuring that the strength and integrity of the glass remain intact.
Mechanical methods of joining glass also provide cleanliness and hygiene advantages, especially laser welding. They eliminate the risk of contamination or damage that can occur with traditional joining methods. This is particularly important in industries where cleanliness is paramount, such as medical or pharmaceutical applications.
Lastly, mechanical methods save time compared to traditional joining methods. Laser welding, for example, is faster than other methods, saving manufacturers precious assembly time and boosting productivity.
Ultrasonic Welding: Overview and Benefits
Ultrasonic welding is revolutionizing the world of joining. With its incredible strength, versatility, and aesthetic appeal, it has become the top choice for many applications. If you need airtight seals, efficient production, or non-destructive joining, look no further than ultrasonic welding. Don’t settle for anything less than the best when it comes to joining glass; choose ultrasonic welding and experience the benefits for yourself.
Ultrasonic welding utilizes high-frequency vibrations to create a bond between two glass surfaces. By applying pressure and ultrasonic vibrations, heat is generated, causing the glass to soften and merge together, resulting in a strong and durable joint.
One of the key benefits of ultrasonic welding is its ability to create hermetic seals. The joints are airtight and watertight, making them perfect for applications that require a barrier against gases or liquids. Additionally, the absence of adhesives or foreign substances ensures a clean and aesthetically pleasing finish.
Speed and efficiency are another advantage of ultrasonic welding. The process is completed in seconds, making it ideal for mass production or high-volume manufacturing environments. Compared to traditional methods, it offers significant time savings and increased productivity.
Furthermore, ultrasonic welding is non-destructive, preserving the integrity of delicate or fragile materials. Manufacturers can ensure the quality of their glass products without compromising their structural integrity.
Ultrasonic welding also offers versatility in joining different types of glass. Whether it’s soda-lime glass, borosilicate glass, quartz glass, or even specialty glasses like tempered or laminated glass, ultrasonic welding can handle it all. This flexibility allows for a wide range of applications in various industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Method for Joining Glass
When it comes to joining glass, there are several factors that need to be considered to ensure the best method is chosen. These factors include strength and durability, transparency, time and cost, temperature resistance, compatibility, and ease of application.
Strength and durability are crucial considerations when selecting a method for joining glass. Different methods offer varying degrees of strength, so it’s important to choose a method that can withstand the intended use of the glass. For applications that require exceptional strength, options such as UV-curing adhesives or mechanical fasteners may be the best choice.
Transparency is another important factor to consider. In certain applications like architectural glass or display cases, an invisible joint is desired to maintain the aesthetic appeal of the glass. In these cases, methods like optical adhesives or solvent bonding can create seamless and transparent joints.
Time and cost constraints should also be taken into account. Adhesive bonding may require curing time before achieving full strength, while mechanical fasteners provide immediate bonding. Additionally, some methods may require specialized equipment or skilled labor, which can increase the overall cost of joining glass. It’s important to consider these factors in relation to your project timeline and budget.
Temperature resistance is critical for environments with significant temperature fluctuations. Methods such as thermal bonding or ceramic frit bonding are known for their excellent temperature resistance and are suitable for high-temperature applications.
Compatibility between the joining method and the type of glass being used is essential. Different types of glass have varying properties that may affect the choice of joining method. Ensuring that the chosen method bonds well with the specific type of glass being used will result in a strong and reliable bond.
Lastly, ease of application should be considered, especially for DIY projects or small-scale applications. Adhesive bonding or UV-curing adhesives often require minimal tools or equipment and are user-friendly. Welding or soldering, on the other hand, may require specialized skills and equipment, making them more suitable for professional applications.
HxZUpKgQ8Gs” >
Conclusion
In conclusion, the realm of glass joining is a captivating one, offering an array of methods to forge robust and enduring bonds between glass pieces. From adhesive bonding to mechanical fastening, thermal joining to laser welding, and ultrasonic welding, each technique brings unique advantages tailored to specific applications.
Adhesive bonding reigns supreme for its remarkable versatility in uniting different types of glass while bestowing aesthetic benefits and fortifying against vibrations and shocks. Meanwhile, thermal joining seamlessly fuses glass joints with unparalleled precision, making it a favored choice in industries like automotive and construction. Welding empowers the creation of intricate structures by delivering strength and accuracy when joining glass with other materials. Laser welding elevates precision to new heights with immaculate welds and meticulous control over heat input. Lastly, ultrasonic welding excels in swiftly and efficiently forming hermetic seals.
When selecting a method for glass joining, it is crucial to consider factors such as strength, transparency, time/cost constraints, temperature resistance, compatibility with the type of glass employed, and ease of application.
All in all, comprehending the various methods of glass joining unlocks a world brimming with possibilities across industries spanning from architecture to electronics. The versatility and efficacy of these techniques ensure that glass remains a malleable material that can be seamlessly joined for both functional purposes and aesthetic allure.