There’s something oddly satisfying about watching glue work its magic, effortlessly bonding surfaces together. But what happens when water decides to join the party? Does it play nice with glue or throw a wrench in its adhesive powers? Today, we’re diving headfirst into the fascinating world of water and glue to uncover the truth.
Water is like that sneaky friend who can either make things better or worse. It’s a fundamental element that affects all sorts of materials, including our beloved glue. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast, a craft lover, or just someone curious about how everyday objects work, this journey into the relationship between water and glue will have you hooked.
So grab your goggles and put on your lab coat as we explore the mysteries behind how water can strengthen or weaken those sticky bonds. We’ll also share some practical tips to help you achieve optimal results when working with these magical substances.
Are you ready for an adhesive adventure like no other? Let’s dive in and finally answer the age-old question: does water affect glue? Get ready to stick around.
What Is Glue?
Contents
Have you ever marveled at how that shattered vase seamlessly comes back to life or how your DIY masterpiece holds its form? The enchantment lies within the captivating world of glue. Glue, an adhesive substance, possesses the power to bond materials together, forging unbreakable connections. Delve deeper into the realm of glue and discover the myriad of types available.
Glue manifests in various forms: liquid, gel, or solid stick. Its composition is derived from natural or synthetic polymers like cellulose, polyvinyl acetate (PVA), or epoxy. Each variant possesses distinct properties and characteristics, rendering them suitable for specific applications.
Water-based glue stands as a common type susceptible to water’s influence. Comprising primarily water infused with polymers and adhesives, this glue absorbs moisture upon contact. Consequently, its adhesive properties diminish, weakening the bond. Traditional white or school glue, often soluble in water, falls into this category.
Despite this vulnerability, not all glues succumb easily to water’s impact. Epoxy or super glue, for instance, possess waterproof qualities due to their chemical composition. These glues resist moisture infiltration effortlessly, remaining unscathed in watery environments. However, prolonged exposure may still erode their strength over time.

To ensure project longevity and robustness when faced with water, meticulous consideration of glue type and material selection is imperative. Porous substances such as wood or fabric readily absorb moisture, compromising the glue’s efficacy. Conversely, non-porous materials like glass or metal exhibit greater resilience to water’s effects, preserving a steadfast bond.
To fortify the endurance and effectiveness of glued items immersed in water, opt for waterproof glues or supplement with protective measures like sealants or coatings. This strategic approach ensures that the bond remains resolute even in damp conditions.
Types of Glue
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue is like a superhero for crafts and school projects. It dries clear and is perfect for sticking paper, cardboard, or lightweight fabrics together. While it’s not completely waterproof, it can handle a bit of moisture without losing its stickiness. So, if you accidentally spill some water on your PVA-glued masterpiece, don’t worry too much – just avoid soaking it. PVA glue forms a strong bond with porous materials by penetrating the surface and drying to create a solid connection. However, excessive exposure to water can cause the glue to soften and weaken, leading to the potential failure of the bond.

Epoxy Glue:
Epoxy glue is like the tough guy in the glue world. It’s the go-to adhesive for repairing ceramics, glass, metals, and plastics. This glue doesn’t mess around with water – it’s highly resistant to H2O. Whether you’re fixing a broken mug or creating a watertight seal, epoxy glue can handle it all. Epoxy glue consists of two components that need to be mixed together before use. Once applied, it forms a chemical reaction that creates a strong, durable bond. Epoxy glue is not affected by water and can even be used underwater for certain applications. Its resistance to water makes it ideal for outdoor projects or areas with high humidity.
Super Glue:
Super glue is the quick-drying magician of the glue family. It forms an instant bond and works great for metal, plastic, and ceramic projects. But watch out – this glue isn’t a fan of water. If you accidentally drop your super-glued item in the sink or spill some water on it, don’t be surprised if the bond weakens or breaks. Super glue, also known as cyanoacrylate adhesive, cures by reacting with moisture in the air. Therefore, exposure to water can accelerate the curing process and cause the glue to lose its effectiveness. It’s best to keep those super-glued items away from water to maintain their strength.
Wood Glue:

Wood glue is like the best friend of carpenters and DIY enthusiasts. It’s specially designed to bond wood surfaces together. While wood glue provides a strong hold when used properly, it can lose its strength if exposed to water for too long. Wood glue typically creates a strong chemical bond with wood fibers, but excessive moisture can weaken this bond and cause the glue to swell or deteriorate. To ensure the durability of wood-glued creations, it’s important to protect them from prolonged exposure to water.
How Does Water Affect Glue?
Water, the mighty force of nature, can wield its power over even the strongest of glues. When water and glue collide, the consequences can be disastrous for adhesive bonds. To understand this dynamic dance between water and glue, we must delve into the world of polymer chains and the delicate balance they maintain.
Glue, in its essence, is a concoction of polymer chains that intertwine to create a formidable bond when dry. However, water has a mischievous nature and seeks to disrupt these chains, weakening the very foundation of the adhesive. The water molecules infiltrate the chemical bonds that hold the glue together, causing it to lose its grip and effectiveness.
Water-based glues are particularly vulnerable to the whims of water. These glues are designed to dissolve in water, rendering them helpless in the face of moisture. When water seeps into a surface bonded with water-based glue, the adhesive loses its stickiness and fails to adhere properly.
Epoxy glues and super glue are more resistant to water’s charms, but they are not impervious. Epoxy glues often contain chemicals that react with moisture to form a stronger bond. However, prolonged exposure to water can still compromise their effectiveness. Super glue, known for its quick-drying magic act, reveals its aversion to water as it loses its stickiness in its presence.
Wood glue, the trusted ally of carpenters, cherishes wood but loathes water. Its bonding strength is unparalleled when it comes to wood projects. Nonetheless, extended contact with water can strip it of its adhesive properties, leaving behind a feeble bond.
To ensure the longevity of our adhesive creations, we must shield them from water’s reach whenever possible. In wet or humid conditions, opting for waterproof or moisture-resistant glues specifically engineered for such environments is crucial.
Water-Based Glues
Water-based glues, as the name suggests, rely on water as their main solvent. This makes them non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternatives to solvent-based adhesives. They are incredibly versatile, able to bond a wide range of materials such as paper, fabric, wood, and even certain plastics. But how does water affect their performance and durability?
Exposure to moisture can indeed have an impact on the adhesive properties of water-based glues. The water present in the glue can reactivate its adhesive qualities, making it tacky again. This can be useful when repositioning or repairing glued objects but can weaken bond strength if the glue gets wet after curing.
However, not all water-based glues are created equal in terms of their resistance to water. Some glues are specifically designed to be waterproof or water-resistant, making them suitable for use in environments where exposure to moisture is common. These glues contain additional additives or ingredients that enhance their ability to withstand water without losing bond strength.
On the other hand, there are water-based glues that are more susceptible to the negative effects of water. Extended exposure to moisture can cause these glues to lose their adhesive properties or experience a reduction in bond strength. It is important to consider the specific requirements of your project and choose a glue that is suitable for the intended application.
To ensure the best performance and longevity of water-based glues, follow proper application and curing procedures. Apply an even layer of glue onto the surfaces to be bonded and allow it to dry and cure fully according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Avoid excessive exposure to water during the curing process to achieve optimal bond strength.
Traditional White Glue (PVA)
Traditional White Glue (PVA), also known as polyvinyl acetate, is a versatile and commonly used adhesive in various applications. It is made by polymerizing vinyl acetate monomers to form long chains of polyvinyl acetate. PVA glue is a water-based adhesive that becomes sticky when wet and forms a strong bond as it dries.
One of the key considerations when working with PVA glue is its relationship with water. While PVA glue is water-soluble and can be easily diluted and cleaned up with water, its bond strength can be affected by moisture. It is important to note that PVA glue is not completely waterproof and may lose its bond strength when exposed to excessive moisture or prolonged water exposure.
However, temporary water exposure or high humidity levels typically do not significantly impact the bond strength of PVA glue. Brief contact with water should not ruin a PVA bond, but it is essential to let the glue fully dry before subjecting it to any moisture.
A unique characteristic of PVA glue is its reversible bond. If a bonded object gets wet again, the glue can soften and lose its adhesive properties. Therefore, it is crucial to protect PVA glued objects from prolonged water exposure. No one wants their masterpiece to fall apart in a rainstorm.
In woodworking, where PVA glue is widely used, it is important to consider the moisture content of the wood. If the wood has high moisture content or is prone to expanding and contracting due to changes in humidity, the bond strength of PVA glue may be affected. For moisture-prone projects, it might be wise to consider alternative adhesive options.
There’s a solution in the form of sealants or top coats. To enhance the moisture resistance of PVA glue, you can seal or coat it with varnish, lacquer, or other waterproof sealants. This additional layer acts as a protective barrier against water infiltration, giving your glued objects a fighting chance against H2O.
Waterproof and Water-Resistant Glues
When it comes to selecting the perfect glue for your project, understanding the difference between waterproof and water-resistant glues is crucial. Whether you’re repairing outdoor furniture, constructing a boat, or working on a craft project, knowing which adhesive will provide the best protection against water and moisture can make all the difference.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the distinctions between waterproof and water-resistant glues and provide valuable tips to help you choose the right glue for your specific application.

Waterproof Glues:
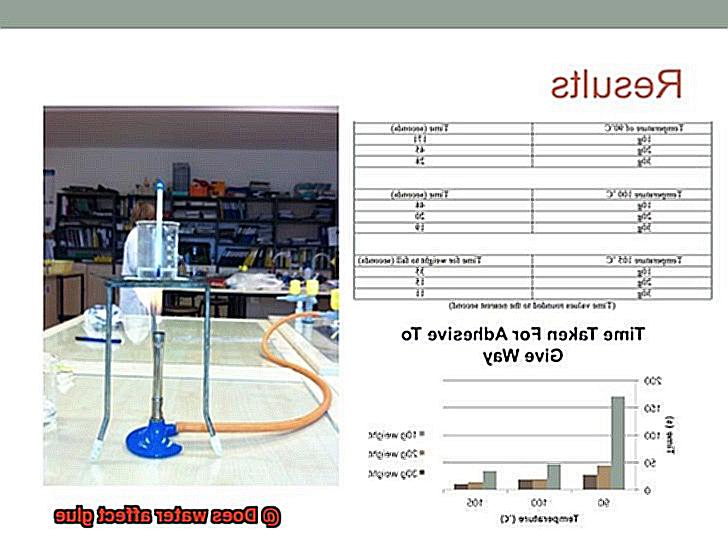
Waterproof glues are the superheroes of adhesives, specially formulated to withstand the effects of water and moisture. They are like warriors that fearlessly battle against water-related challenges.
These glues contain powerful adhesives that create an unyielding bond even when submerged in water or exposed to high humidity levels. Imagine a polyurethane-based glue clinging tightly to surfaces despite the relentless assault of water droplets, or an epoxy adhesive forming an impenetrable barrier against moisture.
Certain types of cyanoacrylate glues, with their extraordinary strength and resilience, also fall under the category of waterproof options.
However, when choosing a waterproof glue, it’s essential to consider factors like temperature fluctuations, water pressure, and the duration of water exposure.
Water-Resistant Glues:
Water-resistant glues are like trusty companions that offer some protection against moisture but may not be fully waterproof. They are reliable allies in indoor projects where there is a lower risk of direct water exposure. Picture wood glue standing strong against mild moisture or occasional splashes, or white glue (PVA) valiantly resisting the advances of water droplets. Certain types of rubber-based adhesives also join this league of water-resistant options. However, when faced with prolonged wet conditions or complete immersion in water, these glues may not hold up as well.
Choosing the Right Glue:
Selecting the appropriate glue depends on the level of water resistance required for your application. If you need to achieve complete waterproofing, like a warrior clad in armor, opt for a waterproof glue. On the other hand, if you only require mild moisture resistance, a water-resistant glue may be your loyal companion. To ensure victory in your bonding quest, carefully read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper surface preparation, skillful application techniques, and patient curing times. These strategic moves will enhance the effectiveness of the glue in water-related situations.
Effects of Prolonged or Excessive Moisture on Glue
The effects of prolonged or excessive moisture on glue can be quite significant. When glue is exposed to water for extended periods, it loses its grip and adhesive properties, causing it to weaken and fail in its bonding capabilities.
One of the main reasons for this is the breakdown of chemical bonds within the glue. Glues contain polymers that form strong bonds when they dry. However, when water enters the equation, these bonds get disrupted, resulting in the glue losing its strength. It’s like trying to hold hands with someone whose fingers keep slipping away – not fun at all.
Moisture can also cause the glue to swell and expand. Many glues are water-based or contain water as a solvent, making them prone to absorbing moisture from their surroundings. This expansion leads to instability, making the glue lose its grip on the materials it’s meant to bond. A slippery situation indeed.
But that’s not all. Excessive moisture creates the perfect breeding ground for mold and mildew. These pesky microorganisms thrive in moist environments and feed on the organic compounds present in glues. Not only do they compromise the adhesive joint, but they also bring health risks and aesthetic nightmares. Nobody wants a moldy mess.
To make matters worse, prolonged exposure to moisture can lead to the degradation of glue over time. Water seeping into the glue breaks down its chemical structure, causing it to lose its adhesion strength and durability. Imagine trying to stick something together with a wet noodle – it just won’t hold up.
But fear not, there are ways to combat these effects and keep your glue game strong. Using waterproof or moisture-resistant glues is a wise move when you know water will be lurking around. It’s also crucial to ensure that the surfaces you’re bonding are clean, dry, and moisture-free before applying the glue. And don’t forget about proper storage – keeping your glues in a dry environment will help them stay in tip-top shape.
The Role of Materials in How Water Affects the Glue
The key lies in the materials involved in the glue-water interaction. In this blog post, we will embark on a captivating exploration of the intricate dance between glues and materials, discovering how they interact with water.
Glue Composition:
The composition of a glue determines its vulnerability to water. Water-based glues, intentionally designed to be water-soluble, contain polymers that break down upon moisture exposure. This breakdown weakens or dissolves the adhesive bond, facilitating easy removal or repositioning of glued objects. On the other hand, waterproof glues are fortified with resins and additives that enhance their resistance to water. These formidable glues retain their adhesive properties even in wet conditions, making them perfect for outdoor or water-exposed applications.
Material Matters:
The materials being bonded together play a pivotal role in how water affects the glue’s adhesive bond. Porous materials like wood or fabric eagerly absorb water, causing them to swell and weaken. Even using a water-resistant glue cannot fully protect these materials from prolonged exposure to moisture.
In contrast, non-porous materials like metal or glass are less susceptible to water damage. For these materials, ensuring proper adhesion becomes paramount rather than protecting against water damage.
Temperature Matters Too:
Extreme temperatures can impact glue’s adhesive properties. Freezing temperatures render water-based glues brittle and ineffective, while heat can soften and weaken various types of glue.
kNgzFVo8xFw” >
Conclusion
In conclusion, the answer to the question “Does water affect glue” is a resounding yes. Water has a significant impact on the effectiveness of glue bonds. When water comes into contact with glue, it can weaken or completely break down the adhesive properties. This happens because water disrupts the chemical composition of the glue, causing it to lose its grip and adhesive strength.
Water acts as a formidable foe to glue, infiltrating its molecular structure and compromising its ability to stick things together. It’s like a stealthy infiltrator that sneaks in and sabotages the bond, leaving behind nothing but disappointment and frustration.
Imagine trying to repair a broken ceramic mug with glue, only to have it fall apart again when exposed to even the slightest amount of moisture. It’s like fighting an uphill battle against an invisible enemy that is determined to undermine your efforts.
The relationship between water and glue is one of incompatibility; they simply don’t mix well together. Like oil and water, they repel each other, creating a barrier that prevents them from forming a strong and lasting bond.
So next time you’re working on a project that requires glue, be mindful of its arch-nemesis: water. Keep your materials dry and free from moisture to ensure that your adhesive bonds remain intact.
In conclusion, water does indeed affect glue in a detrimental way. It weakens its adhesive properties and compromises its ability to create strong bonds.






