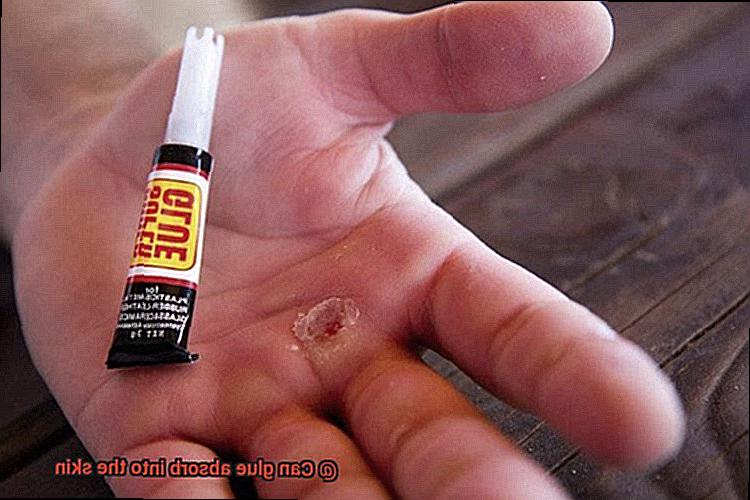
We’ve all been there – a glob of glue on our skin, whether from an artsy project gone wrong or a clumsy mishap. But have you ever wondered what happens when that sticky stuff makes contact with your delicate skin? Can it actually seep into your body and cause trouble?
In this blog post, we’re diving deep into the potential risks of glue coming in contact with your skin. We’ll unravel the science behind glue composition and investigate whether it has the sneaky ability to be absorbed into your precious skin. Brace yourself for some eye-opening insights.
Glue, in all its forms, is designed to stick things together. It’s made up of a polymer base, solvents, and other fancy chemical compounds depending on its purpose. While some glues are safe for skin contact, others can pose risks you need to know about.
Your skin is a superhero – it’s the largest organ in your body and acts as the first line of defense against external substances. Normally, it does an awesome job at keeping out harmful stuff. But when glue enters the picture, things get complicated.
One major concern is whether glue can be absorbed by your skin. Your skin has three layers: the epidermis (the outermost layer), the dermis (the middle layer), and the subcutaneous tissue (the deepest layer). Glue can sneak through that top layer (the epidermis), especially if you have cuts or weak spots in your skin’s armor.

The ability of glue to be absorbed depends on various factors like its ingredients, solvent type, and how long it stays in contact with your skin. Some solvents can help those glue components penetrate deeper into your precious epidermis – not good news for you.
Once that sneaky glue gets absorbed, it can lead to anything from mild irritation to full-blown allergic reactions. Some glues contain nasty chemicals that can cause burns, rashes, and even damage to the deeper layers of your skin. And if that glue manages to make its way into your bloodstream? Yikes. It could spell trouble for your overall health.

In the upcoming sections, we’ll dig even deeper into these risks. We’ll explore the potential health effects of glue absorption and arm you with practical tips to minimize the chances of skin contact. Trust us, it’s crucial to be in the know about these dangers and take steps to keep your skin happy and healthy
What is Glue?
Contents
Glue, a seemingly ordinary substance, holds the power to unite materials and repair broken objects. But what exactly is it? How does it work? In this captivating article, we will delve into the intricate world of glue, unraveling its composition, diverse types, and the science behind its formidable bonding capabilities. Whether you are a DIY enthusiast or simply curious about the wonders of adhesive technology, prepare to become a glue aficionado.

Composition of Glue:
- Polymers: Glue harbors polymers – large molecules composed of repeating subunits. These polymers foster robust molecular bonds between surfaces when the glue dries, resulting in unyielding adhesion.
- Solvents: Many glues contain solvents that dissolve and disperse adhesive properties. These solvents enable even distribution and adherence to different materials.
- Fillers or thickeners: Certain glues incorporate fillers or thickeners to confer specific textures, preventing unwanted dripping or running.
- Additives: Supplementary ingredients enhance glue performance, endowing it with qualities such as flexibility, water resistance, or rapid drying.

Different Types of Glue:
- School glue (PVA): A water-based adhesive commonly employed in arts and crafts projects. Its child-friendly nature allows for effortless removal with water.
- Super glue (cyanoacrylate): This speedy adhesive forms an immensely strong bond upon contact with moisture.
- Epoxy: Consisting of a resin and hardener, epoxy is a two-part adhesive renowned for its unmatched bond strength, particularly useful for bonding metals and plastics.
- Wood glue: Tailor-made for woodworking ventures, wood glue delivers a powerful bond and dries transparently.
How Glue Works:
Application: Glue is spread evenly or applied selectively onto the surfaces intended for bonding.
- Drying: As the glue dries, solvents evaporate, leaving behind adhesive substances. Polymers then forge sturdy molecular bonds with materials, establishing a secure connection.
- Curing: Certain glues necessitate additional time to fully cure and reach maximum strength. Heed the manufacturer’s guidelines concerning drying and curing periods.
Safety Considerations:
- Skin contact: Although most glues are not readily absorbed by the skin, industrial adhesives or adhesive removers may pose a higher risk. To ensure safety, minimize direct skin contact and employ protective measures when handling such substances.
- Allergic reactions: Glue can trigger skin irritation or allergic responses in susceptible individuals. In case of adverse reactions, wash the affected area with soap and water, seeking medical attention if necessary.

Can Glue Absorb Into the Skin?
Glue is a versatile adhesive with remarkable bonding capabilities. However, understanding the potential risks associated with glue and skin contact is essential.
Different Types of Glue:
To comprehend whether glue can absorb into the skin, we must consider the various types available. Let’s explore three commonly used adhesives: superglue, epoxy glues, and polyurethane-based glues.
Superglue:
Known for its fast-drying and strong adhesive properties, superglue typically does not absorb into the skin. However, it can still cause irritation and damage if not handled properly. Avoid applying superglue to sensitive areas or broken skin.
Epoxy Glues:
Epoxy glues consist of two components that create a durable bond when mixed. They are generally safe for external use on intact skin but can cause irritation and hinder healing if applied to broken or damaged skin.

Polyurethane-Based Glues:
Favored in woodworking and construction, polyurethane-based glues possess strong adhesive properties. While they do not absorb into the skin, some individuals may experience skin irritations or allergic reactions. Protect yourself by wearing gloves and clothing to minimize skin contact.
Preventing Adverse Effects:
Even if glue does not absorb into the skin, it can still have negative effects if left on for too long. Glue residue can lead to irritation, redness, or allergic reactions. Promptly remove any glue from the skin using soap and water or an adhesive remover.
The Composition of Glue
Glue, that sticky substance we often take for granted, is actually a marvel of science and engineering. Have you ever wondered what makes glue so effective at bonding objects together? In this section, we will explore the composition of glue and uncover the fascinating components that give it its extraordinary adhesive properties.
At the heart of glue lies polymers, long chains of molecules that have a remarkable ability to cling to surfaces. These polymers can be either natural or synthetic, each with their own unique qualities. Natural polymers, such as casein derived from milk or collagen from animal tissues, have been used for centuries. On the other hand, synthetic polymers like polyvinyl acetate (PVA), polyurethane, cyanoacrylate, and epoxy resins have revolutionized the world of adhesives.
But glue isn’t just about polymers. To enhance its adhesive capabilities and durability, glues often contain a variety of additives and chemicals. Let’s take a closer look at some of these key components:
- Solvents: Glue can sometimes be too thick to spread or apply easily, so solvents are added to thin it out. Water, ethanol, acetone, and toluene are common solvents found in various types of glue.
- Plasticizers: To ensure that glued items remain flexible and intact over time, plasticizers are incorporated into the glue formulation. These substances prevent the glue from becoming brittle and help maintain its elasticity.
- Thickeners: Some glues need a little extra viscosity to prevent them from running or dripping when applied. Thickeners come to the rescue by increasing the thickness of the glue, allowing it to stay put.
- Preservatives: To protect against degradation caused by bacteria or fungi, preservatives are added to glue formulations. This ensures that the adhesive properties of the glue remain intact for years to come, providing a long-lasting bond.
It’s important to note that different types of glue may have different compositions. For instance, super glue is typically composed of cyanoacrylate monomers, which rapidly polymerize upon contact with moisture, creating an incredibly strong bond.
Understanding the composition of glue goes beyond mere curiosity; it also has implications for our safety. Some glues may contain harsh chemicals or allergenic substances that can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions. It is crucial to always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety precautions when working with glue. In case of accidental skin contact, washing the affected area with soap and water is generally recommended, with medical attention sought if necessary.
Glue’s Ability to Penetrate the Skin
Glue, that unsung hero of countless DIY projects and repairs, possesses an incredible ability to bond materials together. However, one question often lingers: can glue penetrate the skin? In this blog post, we will delve deep into the world of glue and explore its interaction with our skin. From super glue to epoxy resin, we will uncover the potential risks associated with glue and provide tips on how to stay safe.

The Different Faces of Glue:
Not all glues are created equal when it comes to skin contact. Let’s examine two popular types:
- Super glue: Renowned for its remarkable bonding powers, super glue may adhere to the surface of your skin but lacks the ability to penetrate deeper layers. However, if you have any open cuts or wounds, super glue can seep in and cause irritation or damage. To avoid infection, it is crucial to clean and disinfect wounds before applying super glue.
- Epoxy resin: While favored for crafts and repairs, epoxy resin is not skin-friendly. This adhesive can provoke allergic reactions and irritation upon contact. To safeguard your skin, it is best to avoid direct contact with epoxy resin altogether.
Medical Adhesives: The Safe Bet
When it comes to adhesives designed for skin contact, medical adhesives reign supreme. These specialized adhesives undergo extensive testing to ensure their safety and effectiveness in wound closure and surgical procedures. They adhere securely without causing harm or irritation to intact skin.
Safety First:
To minimize the risk of glue penetrating your skin, exercise caution when using any adhesive. Follow the safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer and prioritize avoiding skin contact whenever possible. If accidental contact occurs, wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and water.
Conclusion:

While glue can stick to the surface of your skin, its ability to penetrate deeper layers is generally limited. However, certain factors such as open wounds or allergic reactions can increase the risk of glue causing harm or irritation. By understanding the different types of glue and their potential risks, you can take the necessary precautions to keep your skin safe during your crafting adventures.
Potential for Absorption in Certain Glues
Today, we’re going to explore a topic that often goes unnoticed but poses potential risks: absorption in certain glues. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or a weekend warrior, understanding how glues can interact with our skin is crucial for staying safe during your creative endeavors. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of glue absorption.
Absorption and Solvents:
Did you know that some glues contain solvents? These powerful substances are used to dissolve other materials and enhance the effectiveness of glue. However, when these solvents come into contact with our skin, they have the ability to penetrate through the outer layer and potentially enter our bloodstream. It’s like a covert operation happening right under our noses. That’s why it’s vital to be aware of this potential risk lurking within our craft supplies.
Factors Affecting Absorption:
The extent of absorption depends on several factors. Firstly, thinner glues with low viscosity are more likely to be absorbed compared to their thicker counterparts. So, when working with glues that have a watery consistency, exercise caution and take necessary precautions to protect your skin from their sneaky infiltration.
Furthermore, glues formulated for skin contact, such as medical adhesives, may have a higher potential for absorption. These adhesives are specially designed to adhere better to our skin, making them more likely to seep through our protective barrier. Always read product labels and choose the appropriate glue for your specific project to minimize any hidden dangers.
Understanding Your Glue:
Not all glues have the same potential for absorption. It is essential to consider the specific product you are using and its ingredients. Take the time to research and select glues that prioritize safety and minimize potential risks. Don’t let yourself fall into the trap of using a glue that could potentially harm your skin and overall well-being.
Safety Tips:
To keep yourself protected while working with glues, here are some valuable safety tips:
- Wear protective gloves: A simple pair of gloves can act as a formidable barrier between your skin and any potentially harmful substances lurking in the glue.
- Work in a well-ventilated area: Adequate ventilation helps reduce the inhalation of fumes and decreases the chances of skin contact with potentially dangerous glues.
- Follow instructions: Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safe usage and disposal of glue products. They were created to keep you safe and informed.
Skin Irritation and Allergic Reactions
Glue is a versatile adhesive that we commonly use for arts and crafts or household repairs. However, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with skin contact. In this article, we will delve into the world of skin irritation and allergic reactions caused by glue. By understanding these risks and implementing preventive measures, you can keep your skin safe while using glue.
Skin Irritation:
When glue comes in contact with our skin, it can cause irritation, resulting in redness, itching, and a burning sensation. The severity of the irritation depends on factors such as the type of glue used, the duration of contact, and individual sensitivity. People with higher sensitivity to certain chemicals present in glues are more prone to experiencing skin irritation.
Allergic Reactions:
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions when exposed to certain components of glue. These reactions occur when our immune system overreacts to the substances. Symptoms can range from mild, like redness and itching, to severe, including swelling, hives, and difficulty breathing. While not everyone will have an allergic reaction to glue, those with a history of allergies should exercise extra caution.
Preventive Measures:
- Read instructions: Always read and follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer before using glue. This will give you important information about potential hazards and safety precautions specific to that product.
- Ventilation is key: Ensure that you’re using glue in a well-ventilated area or with proper air circulation. This helps reduce the inhalation of fumes that could irritate your skin or respiratory system.
- Protect your hands: Wear protective gloves to create a barrier between the glue and your skin. This is especially important if you have a history of skin sensitivity or allergies.
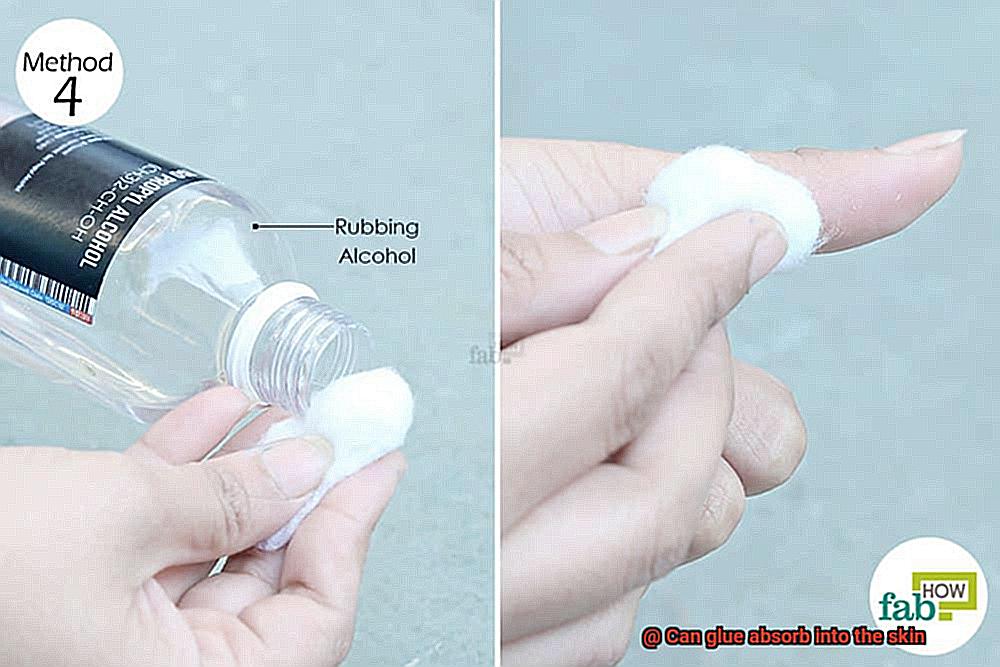
- Prompt action: If glue accidentally comes into contact with your skin, don’t panic. Wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and water. Avoid scrubbing vigorously, as this can further irritate the skin.
- Seek medical attention: If skin irritation persists or if you experience severe symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as swelling or difficulty breathing, seek immediate medical attention.


Safety Precautions When Handling Glue
Glue is a remarkable tool for crafting and DIY projects, but it’s important to handle it with caution to avoid any potential risks or accidents. When working with glue, there are several safety precautions you should keep in mind to ensure your well-being:
- Glove up: Always wear protective gloves when handling glue to prevent direct contact with your skin. This will minimize the chances of the glue being absorbed into your skin. You definitely don’t want to end up with sticky fingers for days.
- Wash it off: In case glue comes into contact with your skin, don’t panic. Immediately wash it off with soap and water. Avoid peeling or pulling the glue off, as this may cause further damage to your skin.
- Breathe easy: Some glues emit strong fumes that can be harmful if inhaled for an extended period. It’s crucial to work in a well-ventilated area to ensure proper air circulation. Open those windows and let the fresh air flow.
- Follow instructions: Each type of glue comes with its own set of safety instructions provided by the manufacturer. Take the time to read and follow these instructions carefully. They will guide you on how to handle and store the glue safely.
- Seal it tight: After completing your glue project, make sure to close the container tightly. This prevents spills and keeps the glue fresh for future use. Store it in a cool and dry place away from children and pets.
- Less is more: Avoid using excessive amounts of glue. Not only does this waste precious adhesive, but it also increases the chances of spills or accidental contact with your skin.
- Allergic reactions beware: If you experience any allergic reactions or unusual symptoms after coming into contact with glue, seek medical attention immediately. It’s always better to be safe than sorry.
- Scrub it off: After finishing work with glue, remember to wash your hands thoroughly. Even if you’ve been wearing gloves, there might still be some residue lingering on your skin. So, scrub away that stickiness and keep your hands clean.
- Eyes on the prize: Glue and eyes don’t mix well. Avoid getting glue anywhere near your eyes, as it can cause irritation and potential damage. However, if the unthinkable happens and glue accidentally gets into your eyes, don’t panic. Flush them with clean water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical help promptly.
VlOVnfN3vSE” >
Also Read: Is Elmer’s Glue Toxic?
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is important to understand that glue can indeed absorb into the skin. This means that if you come into contact with glue and it gets on your skin, there is a possibility that it will seep into the layers of your skin. This can lead to potential health risks and complications.
The skin acts as a protective barrier for our bodies, but it is not completely impermeable. Glue contains chemicals that are designed to bond materials together, and these chemicals can penetrate the skin under certain circumstances.
Once the glue enters the skin, it can cause irritation, redness, and even allergic reactions in some individuals. The severity of these symptoms depends on several factors such as the type of glue used, duration of exposure, and individual sensitivity.
Furthermore, certain types of glue may contain toxic substances such as formaldehyde or solvents that can be harmful when absorbed into the body. Prolonged or repeated exposure to these substances through skin absorption can have long-term health effects.
To prevent glue from absorbing into your skin, it is essential to take precautions when working with adhesive products. Wearing protective gloves and using proper ventilation in well-ventilated areas are recommended. If you do get glue on your skin, promptly wash the affected area with soap and water to remove any residue.
In summary, while our skin provides a barrier against many substances, glue has the ability to absorb into the skin under certain conditions.